Co-Author: Liam Quinn, SVP / Senior Fellow, Client Solutions Group, Dell Technologies
Imagine a framework where devices can share computing resources and services seamlessly with other devices and leverage programmable network capabilities to optimally analyze the data and deliver business outcomes. IoT, social media and new edge deployments enabled by 5G and AI/ML (Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning) are driving cloud applications to move to distributed edge. Future usage models will require new architectures that enable highly collaborative data processing environment with intelligent and fluid sharing of compute resources and mobility of applications across devices. We believe new architectures and rapid industry innovations are required to enable seamless collaboration and data sharing at the edge.
Current Edge Use Cases and Technology Innovations
Current edge use cases are moving data processing closer to end devices. For example, content distribution moves data from cloud to edge and leverages content delivery networks (CDN) for caching of content closer to the end users. IoT and social media use cases lead to consuming and generating data at the edge. This data is analyzed at the end devices or an edge-cloud to deliver the right outcome. Edge-cloud may be on-prem, a co-location facility or offered “as-a-Service” by a service provider. The use cases and deployment scenarios vary across industry verticals that includes home automation, ADAS, smart factories, retail, oil and gas, agriculture and enterprises.
Growth in number of IoT devices, cost of data transport and mission critical use cases drove this shift to move processing of data from cloud to edge. The enabling technologies are summarized below.
- High-Performance Client Devices: Client devices have CPU cores and hardware acceleration capabilities to process data locally and execute ML inferencing models. New embedded sensors and sensor fusion is driving continuous improvement in intelligence, location and context-aware capabilities. This combined with AI/ML is creating client/edge ready and agile applications.
- Network Edge-Cloud: Cloud applications and data processing is moving to network-edge and edge-clouds to process data closer to end devices at lower latency. Improvements in compute performance/watt is enabling increased processing capabilities. Data management control planes have an important role in decision on where optimized data processing will occur.
- AI/ML and Accelerators: AI/ML frameworks and low-power hardware accelerators are emerging to enable inferencing at the edge, while compute intensive operations of training are performed at the centralized cloud. These accelerators are embedded in smart end devices and network edge platforms. The trained ML model is delivered at the edge to enable inferencing close to the point of data generation.
- 5G Cellular Network: The emerging 5G network enables high speed wireless network pipes and lower latency for diverse workloads, leveraging existing and new spectrum. Virtualization of RAN (vRAN) enables radio processing to shift from custom devices at cell towers to standard x86 servers with hardware accelerators for aggregated RAN processing. It enables performance scaling for large number of micro-cells, seamless mobility and billions of end-devices.
- Network Slicing: The growth in number of edge applications and distribution of processing between cloud and edge is driving next level of innovation in network-slicing capabilities. This enables connectivity with guaranteed SLA between an end-device and a backend application. The application may be running at Telco network edge or in the cloud.
- Programmable Networks: Programmable networks are emerging to enable seamless mobility of users and re-configuration of network slices. They also enable moving an application seamlessly from cloud to edge, along with the associated networking and security services.
- SD-WAN: Software Defined WAN has emerged to enable edge to cloud connections with multiple quality of service options. Data is distributed across these WAN connections to deliver optimal application performance.
- Wi-Fi and Cellular Convergence: Requirements around seamless end-user mobility is driving innovation in Wi-Fi and cellular convergence with next generation Wi-Fi and Private-LTE / CBRS (Citizen Broadband Radio Spectrum). New Dell Edge devices with embedded sensors and smart antenna/radio switching are key elements to enabling this seamless experience based on workload applications and usage models.
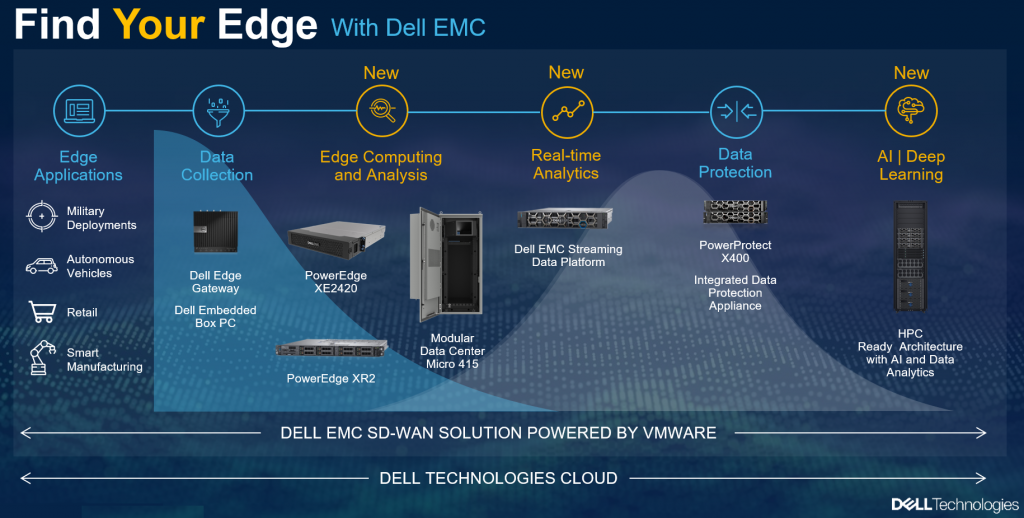
Dell Technologies is innovating in each of the above areas and collaborating with Telcos, Service Providers and Cloud providers to deliver critical capabilities to end users. The edge and data center infrastructures are designed to scale with smart client devices, high performance PowerEdge servers, Hyper Converged Infrastructure (HCI), and dense GPU Platforms.
Dell Technologies recently announced innovations that highlight these capabilities:
- PowerEdge XE2420 servers offer dense compute and robust security for edge deployments.
- Modular Data Center Micro 415 brings data center to far-reaching and rugged environments.
- Dell EMC iDRAC9 software brings remote access for a uniform, more secure server management experience from the edge to the core to the cloud.
- Dell EMC Streaming Data Platform stores and analyzes edge data.
- Network Slicing Capabilities enable software on client devices to configure network slices all the way from user applications to network edge or cloud for guaranteed performance.
Future Edge Usage Models and Architectural Shifts:
With the dramatic growth in data as well as edge devices, the current edge infrastructure doesn’t scale well for extreme collaboration environments in the future. The next generation usage models around real-time content sharing, gaming, AR/VR, autonomous vehicles, drones and robotics are driving highly collaborative environments where information will be stored, distributed and analyzed across the end devices and the network edge. For example, users watching a game or concert in a stadium want to share locally captured content in real-time with other users. Distributed consumers want to collaborate using online gaming combined with virtual reality (VR) capabilities. This will leverage peer-to-peer communication and embedded AR/VR capabilities in the client devices. Autonomous vehicles, drones and robotics will take the edge information processing and direct device-to-device communication to next level.
The figures below show this evolution from today’s Edge-to-Cloud architecture to future Intelligent & Elastic Compute Architecture.
Current Technology Enablers:
- Hardware acceleration
- 4G → 5G, programmable networks
- SD-WAN
- WI-FI and cellular convergence (5G, CBRS)
Future Technology Enablers:
- AI-enabled elastic compute
- Devices with system on chips modules, micro-AI
- Multi-tenant network slicing
- Decentralized/trusted compute and data fabric
- Intelligent arbitration across peer-to-peer devices
The future architecture will build on the capabilities of current high performance client devices, AI/ML, and network edge, but will also require a new range of innovations to deliver highly intelligent devices, elastic compute environment and decentralized storage infrastructure that adapts to demands of next generation workloads. There are various industry efforts underway to drive these innovations and Dell Technologies is developing solutions for AI-driven Elastic Compute.
- Intelligent Client Devices: Highly integrated “system-on-chip” modules are emerging that will serve as the building blocks in client and edge devices including wearables, video surveillance, industrial and automotive systems. These ASICs enable highly intelligent devices with right amount of compute, memory, storage and AI/ML capabilities. System-on-chip modules are integrating micro-AI and micro-Accelerators with software frameworks to enable ease of AI application development. These silicon, power advancements and software frameworks will enable an environment where device capabilities will be treated as virtual. Think of an “elastic model” where devices and network collaborate to deliver the experience requested by an end user, and it leverages collective capabilities across peer devices and network edge.
- Decentralized Data Fabric: Storage architecture will become decentralized enabling the end users and edge clouds to contribute storage capacity. The data will be distributed across locations based on geo-awareness, performance, security and regulatory policies (e.g. GDPR).
- Multi-tenant and Trusted Compute: Trusted computing frameworks are emerging to enable optimal placement of application execution and associated data. Processor vendors are embedding security features (e.g. Intel SGX, AMD SEV, ARM TrustZones) to create a trusted execution environment for applications in multi-tenant environments.
- Data Center Disaggregation and Memory Fabrics: Enterprise infrastructure is evolving to a disaggregated composable architecture where in CPU, memory, IO, accelerators are disaggregated using a memory-based fabric. This enables a software defined infrastructure where in compute nodes are dynamically composed to adapt to the workload needs. Some technology innovations in this area are GenZ and CXL for future memory fabrics, persistent memory (PMEM) for high speed storage and high-bandwidth memory (HBM) for future embedded memory.
- vRAN and Dynamic Network Programmability: vRAN (Virtual RAN) and programmable networks will evolve to enable guaranteed SLA on peer-to-peer connections across devices and applications.
- AI/ML driven Resource Optimization: The streaming telemetry from client and enterprise infrastructure will leverage distributed analytics for real time reconfiguration of infrastructure and applications.
These technology innovations will enable a grid-like elastic compute environment. The opportunity is to make intelligent use of distributed resources, network transports and mobile connectivity to enable a collaborative environment, where in device capabilities and applications are treated as virtual entities and peer-to-peer architectures enable elastic composition of services. AI/ML will serve as the centralized brain to orchestrate applications across secured and distributed resources. Companies that lead this innovation will succeed in the next generation of AI-driven elastic and decentralized edge. Dell Technologies is driving these innovations across its solution offerings, industry standardization efforts and engaging with partners to both innovate and integrate technologies in Dell platforms.