Everyone in IT knows about Microsoft Patch Tuesdays. It refers to that one day every month when Microsoft provides software updates for its Windows OS, browsers and business applications. These updates fix either security vulnerabilities or bugs in the software. On the most recent Patch Tuesday in April, Microsoft provided updates to fix 113 vulnerabilities across its different software products. In this blog, we’re going to focus on how to better manage updates for Microsoft Windows 10.
Windows 10 divides updates into two categories, with two different release cadences:
- Feature updates – which relate to improvements and new capabilities and are released twice a year, during spring and fall, also known as “semi-annual” releases.
- Quality updates – which are Windows security improvements and are also known as “cumulative updates”. These usually happen every second Tuesday of every month, also known as “Patch Tuesday”, with the most recent one being on April 14, 2020.
Occasionally, if there’s a high-risk security vulnerability discovered, Microsoft releases an out-of-band patch, i.e. in between Patch Tuesdays, that should be applied immediately.
A recent out-of-band security update was released in March 2020 to address an SMB vulnerability referred to as ‘SMBGhost’ or ‘EternalDarkness’ by security vendors. This ‘wormable’ Windows vulnerability, CVE-2020-0796, impacted the Microsoft Server Message Block 3.1.1 (SMBv3 network communications protocol). (Read more about it in our blog Pay Attention to Cybersecurity Warnings).
Patches are cumulative in Windows 10, meaning that if you miss an update one month, it’s rolled into the patch for the next month.
From a business IT perspective, we want to automate the Windows 10 update process using an endpoint management solution. We also want complete control over the process so that we can specify the update schedule and determine which individual devices or groups of devices receive them.
Windows 10 Patching in Kaseya VSA
Kaseya VSA enables you to automatically deploy Windows patches. It also supports native Windows patching. This allows you to configure Windows update settings in VSA and control how Windows manages its own patching process.
You can also enforce the Windows configuration settings you set up in VSA by automatically reverting to them if a local admin makes changes.
Kaseya VSA and Windows Update Group Policy
Using Kaseya VSA, your IT administrators can apply and remove Windows Update Group Policies and set them on all managed endpoints. They can configure many different Windows Update Group Policy options in VSA, such as:
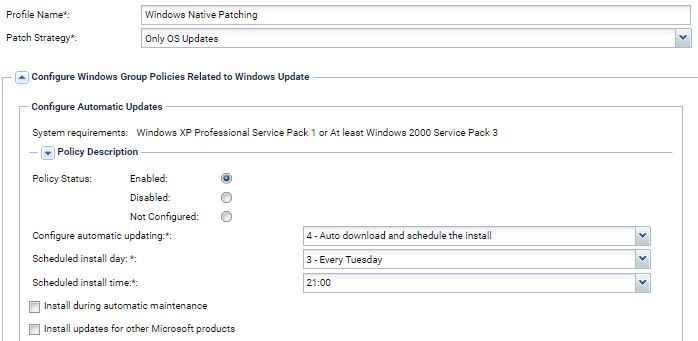
Windows Automatic Updates
This specifies whether a specific computer will receive security updates and other important downloads through the Windows automatic updating service.
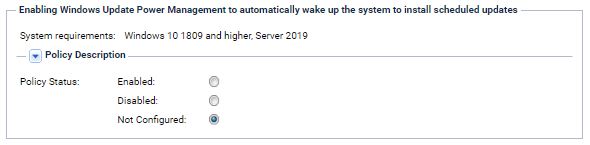
Windows Update Power Management
This allows you to wake up a computer to apply the Windows patch update. This could be very useful if you want to schedule Windows updates for remote worker computers that may be turned off after hours.
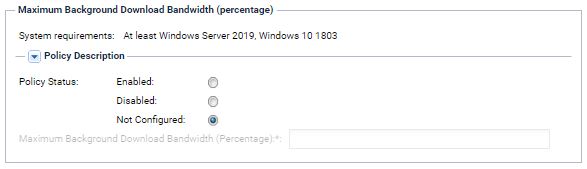
Control download bandwidth
With Kaseya VSA you can also control download bandwidth used for the Windows update. This can be very useful when managing remote worker computers that may be on lower bandwidth home networks.
Windows Patch Management Best Practices
Here are a few best practices for managing Windows patches:
- Execute your scans throughout the week prior to an upcoming Patch Tuesday to ensure you have the latest information available on your endpoints.
- Distribute your scans extensively. This is important since users are mostly working from home and we want to conduct software patch management related tasks during non-peak hours to ensure the tasks can be completed. Kaseya VSA supports scan distribution windows.
- Distribute your patch deployments. It is no secret that Windows patches are beginning to get larger in size (some over 1GB). This can strain not only your server but also your remote user’s network. We highly recommend staggering deployments with 6+ hour distribution windows if you are deploying during business hours.
- Take a look at scheduling deployment times with expanded distribution windows.
- Review new patches as they are released and create a plan to test the deployment of these newly available patches to a test environment or select group of endpoints before you deploy widely to your environment.
To learn more about patching your systems efficiently and improving your IT security with Kaseya VSA, download our checklist 10 Tips to Improve IT Security.





