Updated: April 18, 2024
Published: October 31, 2023
What makes the supply chain a fundamental aspect of the global economy? What is the role of AI in supply chain? How does it shape the way goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed? This article takes a look at using AI in supply chain, and how it’s benefiting related businesses.
List of the Content
- What is AI in supply chain?
- How does AI enhance supply chain optimization?
- AI in supply chain examples
- Benefits of AI in supply chain
- AI in supply chain challenges
- How to apply AI in supply chain?
- Conclusion
WHAT IS AI IN SUPPLY CHAIN?
If someone thinks of AI as some innovation, it’s time to approach it as an indispensable part of many business operations and processes. The integration of artificial intelligence has become vital for companies that would like to produce and deliver products efficiently. Therefore, AI in supply chain emerged as a game changer, contributing to overall economic growth.
Efficient and streamlined supply chains embrace timely delivery of services and goods. By implementing AI, businesses have gained all the required means to improve their services, allocate resources, support productivity, etc.
Considering the experience across different domains, AI in supply chain was among the primary use cases. Many companies realized the need to run their business operations with the latest approaches in the fast-paced market. Bringing AI into supply chain allowed them to handle rising needs with advanced tech solutions. Artificial intelligence can introduce extra efficiency to facilitate data flow among different functionalities and support the main purposes of modern supply chains. Let’s consider some crucial aspects that enable effective business operations and smooth movement of services and goods.
- AI adoption plays a critical role in ensuring product quality. It helps to facilitate quality checks and controls at various stages of production and distribution, preventing defects and recalls.
- Modern supply chains powered by AI are usually flexible and adaptable to changing market conditions. They can quickly respond to shifts in customer demand, regulation changes, or supply chain disruptions.
- Providing services and products to customers when and where they want them is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction. A well-managed supply chain ensures timely and reliable delivery, which can lead to increased customer loyalty.
- AI in supply chain helps in managing inventory levels. They ensure that products are neither overstocked nor understocked, which can reduce carrying costs and prevent stockouts.
- By optimizing the flow of materials, information, and funds, companies can minimize waste, lower production and transportation costs, and ultimately improve their profitability with AI introduction.
- Efficient communication and data sharing enables better decision-making and coordination throughout the supply chain. AI has become an inevitable part of the flow of goods and services.
- AI allows businesses to approach supply chains as a source of ideas. Companies can collaborate with suppliers and partners to develop new products, processes, and technologies, leading to a competitive edge.
- AI adoption also focuses on sustainability and reducing environmental impact. Many companies manage to minimize waste, reduce emissions, and use sustainable sourcing and transportation methods.
- Supply chains have to adhere to various regulations and standards, including safety, environmental, and trade regulations. Ensuring compliance is key to avoiding legal and reputational issues when using AI.
- As businesses expand globally, AI in supply chain helps to support this growth. It focuses on enabling access to new markets and managing international logistics.
- Collaboration is a central purpose of good supply chains. Companies work closely with suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and other partners to streamline operations, share risks and rewards, and achieve common goals with the help of AI.
- Artificial intelligence in supply chains helps allocate resources efficiently by optimizing the use of labor, machinery, and transportation assets.
- A well-designed and well-managed supply chain powered by AI is also a source of competitive advantage. It can enable a company to outperform competitors in terms of cost, quality, delivery speed, and customer service.
Overall, AI in supply chain allows businesses to evolve and meet consumers’ diverse and dynamic needs while addressing the challenges and opportunities of the modern world.
HOW DOES AI ENHANCE SUPPLY CHAIN OPTIMIZATION?
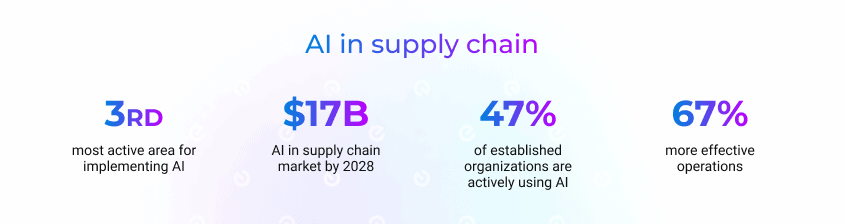
Artificial intelligence has made a profound impact in evolving how businesses manage their supply chain operations. It offers great flexibility to enhance supply chain optimization in many specific ways. Organizations have experienced that AI-powered supply chains are 67% more effective, including reduced risks and lower costs. So, let’s consider some areas to optimize supply chains with AI.
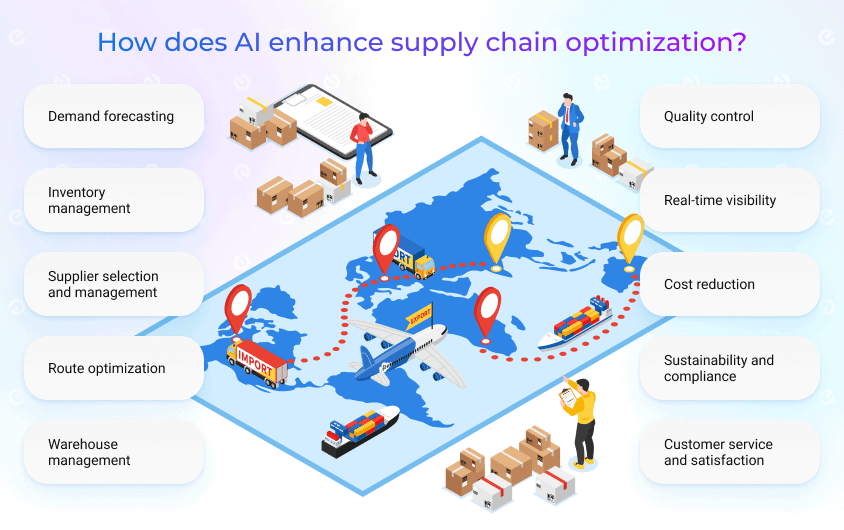
Demand forecasting
AI helps to analyze historical data, market trends, and various external factors to improve demand forecasting accuracy. That enables companies to anticipate customer demand better, reduce excess inventory, and minimize stockouts, resulting in cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Inventory management
AI-powered algorithms can optimize inventory levels, considering demand fluctuations, lead times, and other variables. That reduces carrying costs, prevents overstocking, and ensures that products are available when needed.
Supplier selection and management
AI can assist in evaluating and selecting suppliers based on price, quality, reliability, and location. It can also monitor supplier performance in real time, identify potential issues, and suggest alternatives when problems arise.
Route optimization
AI-driven routing and scheduling algorithms can optimize the delivery routes for transportation fleets, taking into account factors like traffic conditions, weather, and delivery windows. It reduces transportation costs, fuel consumption, and delivery delays.
Warehouse management
AI in supply chain also covers the improvement of warehouse operations by optimizing storage, picking, and packing processes. It can improve order fulfillment accuracy, reduce errors, and increase operational efficiency.
Quality control
AI-based image recognition and machine learning models are used for quality control in manufacturing and distribution. That ensures that defective products are identified early in the process, reducing waste and improving product quality.
Real-time visibility
It provides visibility into the entire supply chain, allowing companies to track the status of shipments, monitor inventory levels, and respond to disruptions quickly. Visibility is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring smooth operations.
Cost reduction
Artificial intelligence can identify cost-saving opportunities across the supply chain through process optimization, energy efficiency, or resource allocation. It can suggest strategies to reduce operational costs without sacrificing quality.
Sustainability and compliance
AI in supply chain helps companies track and improve sustainability metrics by optimizing transportation routes, reducing waste, and identifying eco-friendly sourcing options. Additionally, it can assist in ensuring compliance with industry regulations and ethical standards.
Customer service and satisfaction
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants improve customer services by providing real-time updates on order status, resolving queries, and offering personalized recommendations. It results in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
As a result, AI enhances supply chain optimization by providing data-driven insights, automating decision-making processes, and enabling proactive responses to changes and disruptions. It encourages efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances customer experiences, making it a valuable tool for businesses seeking a competitive edge in today’s complex supply chain landscape.
AI IN SUPPLY CHAIN EXAMPLES
AI implementation within the supply chain is a common market practice. As for the statistics, the global share for such solutions could reach $17.5 billion by 2028. More and more businesses find this investment reasonable and benefit more from adopting AI in new and existing supply chain solutions.
Proceeding with this topic, we also need to discover some known AI in supply chain examples and how they gain popularity in the market.
AWS Supply Chain
It’s a ready-to-use solution introduced by AWS for advancing existing supply chain solutions. It works for unifying data, providing insights, building collaboration, and planning demand. AWS Supply Chain offers a wide set of functionalities to connect existing solutions without re-platforming. That allows teams to leverage data across the chain and automatically outline individual product requirements. It greatly helps retailers optimize their warehouses and increase AI in logistics and supply chain efficiency. Businesses can start with the free trial during the period of 60 days and then go with a pay-as-you-go plan based on actual usage.
Microsoft Supply Chain Platform
Microsoft has introduced a separate platform for advancing supply chains. Businesses can choose between a variety of products to advance new and existing solutions. They specialize in all related areas, from warehouse management to sustainability acceleration. The platform embraces all market changes and meets evolving customer needs. They continue introducing new supply chain products as well as advancing the existing ones. For example, Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management is a known product for its visibility, efficiency, and agility. Besides, Microsoft has a list of trusted partners to share their extensive knowledge and help implement within your organization.
Oracle Fusion Cloud Application Suite
The Oracle product focuses on enhancing automation and AI capabilities to optimize supply chains. They have introduced an integrated platform that can handle complex integrations. The main idea is to enhance the speed and insights without impacting financial accuracy. The new Oracle Fusion Applications Suite updates present AI-powered lead time estimates, an advanced quote-to-cash process, and rebate management capabilities. Oracle works on connecting different areas, including finance and supply chain, based on the latest AI advancements.
IBM Sterling Supply Chain Intelligence Suite
The next tool represents the solution for AI-driven optimization and automation, delivered explicitly for enterprises. Sterling Supply Chain Intelligence Suite helps deal with disruptions through conventional change methods. The components within this suite aid in fostering a digital transformation of the supply chain, enhancing the resilience and sustainability of the supply network, boosting agility, and expediting the realization of value through actionable insights, more intelligent processes, and automation. It has already found its adoption in supply chain mapping, food safety, tracking, etc.
As technology continues to evolve and AI solutions become more sophisticated, the benefits of AI in supply chain management are expected to become even more pronounced. Quick adaptation to changing conditions, consumer demands, and unforeseen disruptions will be a critical competitive advantage for businesses. What’s more, companies always have the opportunity to introduce custom AI-powered solutions covering specific needs.
Would you like to implement AI in your supply chain?
Feel free to contact Existek. Our team of experts knows how to turn your requirements into sophisticated supply chain software powered by AI.
BENEFITS OF AI IN SUPPLY CHAIN FOR THE GLOBAL ECONOMY
Implementing AI technologies in supply chain management can be a strategic move for organizations looking to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving business market. Besides, it’s essential to delve deeper and understand how the supply chain influences the global economy.
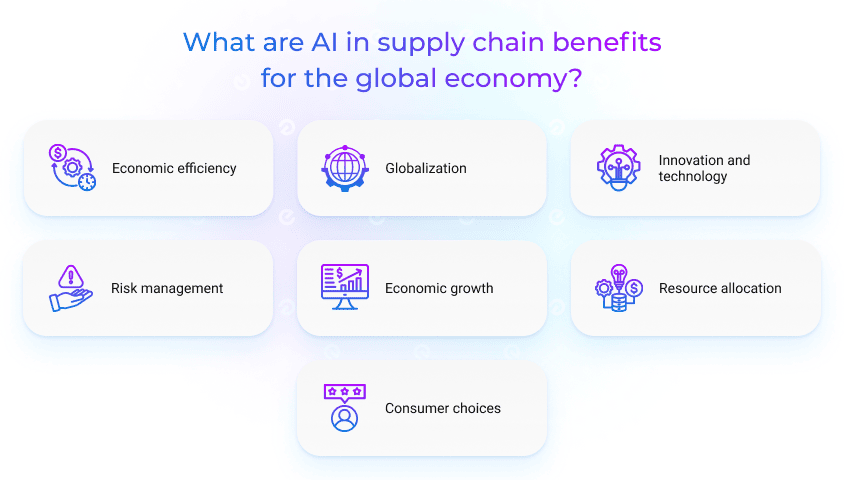
Economic efficiency: When companies can produce and deliver products more efficiently, it contributes to overall economic growth. AI in supply chain and logistics can reduce production costs, minimize waste, and improve productivity. Delivered efficiency leads to lower prices for consumers and higher profit margins for businesses. Streamlined processes, just-in-time inventory management, and optimized transportation reduce costs, making goods more affordable for consumers.
Globalization: The globalization of the supply chain has expanded international trade and economic interdependence. Supply chains enable companies to access global markets, expanding their customer base and revenue potential. Different regions and countries can specialize in producing specific goods, taking advantage of their comparative advantages, which benefits global trade.
Innovation and technology: Companies invest in technology and process improvements to optimize their supply chains, leading to the development of new products, services, and industries. AI empowers innovation in the supply chain by providing insights, optimizing operations, reducing costs, and improving decision-making. These advancements streamline the supply chain and drive sustainability and resilience, making AI a valuable tool for the industry’s future.
Economic growth: AI in supply chain management can significantly improve efficiency, cost savings, and competitiveness. These aspects positively impact a company’s bottom line. When scaled across an entire industry, they contribute to economic growth, increasing productivity and reducing waste, ultimately leading to greater profits and job opportunities. As businesses expand and trade across borders, they create economic value, generate tax revenue, and stimulate investment in infrastructure and services, further fueling economic growth.
Risk management: AI in supply chain management provides the tools and insights necessary to proactively manage risks, increase resilience, and minimize the influence of disruptions on the global economy. By using AI to enhance risk management, businesses can operate more efficiently, reduce waste, and maintain smoother supply chain operations, ultimately contributing to the stability of the global economy. The risk management aspect of supply chains has led to the growth of insurance and financial services industries, supporting risk coverage and business continuity.
Resource allocation: AI tools for supply chains help to allocate resources efficiently by matching the supply of goods and services with consumer demand. This helps prevent resource shortages and surpluses, leading to a more stable and productive economy. Besides, sustainable supply chain practices reduce resource consumption, benefiting both the environment and long-term economic stability.
Consumer choices: The supply chain influences consumer choices by providing a wide variety of products and services. It also affects product availability, quality, and pricing, which can impact consumer spending and overall economic health. As a result, AI in supply chain can lead to competitive pricing, benefiting consumers and boosting purchasing power.
The supply chain’s influence on the global economy is multifaceted, with each aspect contributing to economic growth, efficiency, and resource management. It is a dynamic system that responds to market changes, technological advancements, and global events, playing a pivotal role in shaping the world’s economic landscape.
CHALLENGES OF AI IN SUPPLY CHAIN
Incorporating AI into the supply chain is a complex process that requires a holistic approach. Companies should consider major challenges and develop comprehensive strategies to mitigate risks and maximize the benefits of AI. Overcoming the disadvantages of AI in supply chain requires careful planning, investment, and a strategic approach to its adoption. So here are some main challenges for consideration
Data quality: Supply chain AI systems heavily rely on accurate and up-to-date data. Ensuring data quality, consistency, and accuracy from various sources has always been a significant challenge. Supply chains generate vast amounts of data, and processing it in real time is essential to make timely decisions. Missing data points can be problematic for AI algorithms, especially when they are expected to provide insights or predictions based on complete datasets. Addressing missing data and imputing values accurately is crucial.
Data consistency and integration: Consistency issues can result from different data definitions and formats across systems and departments. Ensuring data is consistent and aligned with business objectives is crucial for accurate analysis and forecasting. Supply chains typically involve multiple stakeholders and systems, leading to data residing in silos. AI requires seamless data integration from various sources to provide a holistic view of the supply chain.
Integration with legacy systems: When some enterprises continue to rely on outdated supply chain systems, it presents a significant challenge when attempting to incorporate AI solutions into these infrastructures. The integration process is laborious, time-consuming, and financially burdensome. The difficulty extends beyond the technical aspect, encompassing the need to guarantee that the AI system comprehends and harmonizes with the intricacies of the established operational procedures.
Data security: The increasing integration of AI and data analytics in supply chain operations has resulted in the aggregation of extensive datasets, some of which may contain sensitive information. This surge in data accumulation has sparked notable concerns about protecting data privacy and identifying cybersecurity vulnerabilities in AI-powered supply chain systems. As a result, it is now imperative to prioritize establishing robust security measures and strict adherence to data privacy regulations. Within this context, safeguarding sensitive data and proactively addressing the cybersecurity risks embedded in AI supply chains have become matters of utmost significance.
Scalability opportunities: As businesses experience growth, their supply chain operations inevitably expand in tandem. It’s important to recognize that an AI solution that functions effectively within the confines of a smaller operation may encounter challenges when faced with the demands of scaling up. That can result in disruptive AI-driven supply chain interruptions. Therefore, it is imperative to prioritize the scalability of AI solutions to ensure sustained success in the long run.
Ethical concerns: AI can raise ethical concerns, particularly regarding decision-making in supply chain processes. Companies have to consider the potential ethical implications of AI-driven decisions and their impact on various stakeholders. The ethical considerations surrounding AI encompass not only the prevention of bias and discrimination but also the need to provide clear, comprehensible, and accountable decision-making processes, particularly in scenarios where vendor relationships and customer experiences are at stake.
The awareness of AI-related challenges in the supply chain is essential for successful implementation, risk mitigation, resource allocation, and ongoing improvement. It enables organizations to approach AI adoption strategically and ensures that AI solutions effectively address supply chain needs.
HOW TO APPLY AI IN SUPPY CHAIN?
The future of AI in supply chain appears to hold great promise, with plenty of upcoming integrations and advancements on the horizon. Nevertheless, it’s crucial for businesses to exercise caution and proactively get ready for the potential emergence of novel challenges. Organizations have to remain vigilant and adapt to the evolving AI landscape to ensure long-term success.
Provided that some business decides on implementing AI within the supply chain, they need to undergo the common AI lifecycle. Let’s consider some of the main stages and what to focus on for companies using AI in supply chain.
Business problem identification
Everything begins by gaining a deep understanding of the current supply chain processes. Along with investigating various AI use cases, the team needs to define clear objectives specific to their business needs. The key is to align AI initiatives with organization’s strategic goals and continually adapt to changing circumstances. It’s important to engage with key stakeholders, such as supply chain managers, procurement teams, and logistics experts, to identify pain points and challenges within the supply chain. Common issues might include high operational costs, inventory management problems, delays, quality issues, or lack of visibility.
Data discovery and preparation
It’s a particular stage to collect relevant data from various sources within the supply chain. This data can include historical sales data, inventory levels, production data, transportation data, quality control data, supplier data, and more. It’s required to ensure that the data is representative of the supply chain processes. Collected data from various sources might contain errors, missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies. Data cleaning and preprocessing involve tasks like data validation, removing duplicates, filling missing values, and transforming data into a consistent format.
Model training and validation
It’s essential to approach model training and validation with a structured and iterative process to achieve the best results. The AI team has to choose the appropriate machine learning or deep learning algorithms based on the nature of the problem. It allows them to create relevant features from the data that help the model understand the patterns and relationships within the supply chain. The training dataset, along with tuned hyperparameters, adjusted model architectures, and different techniques, is used to train AI models. Later, the model’s performance is evaluated on the validation set when generalizing well to new data.
Model scaling and deployment
Once the team gets trained models performing well, it’s time to consider scaling it for real-world use. As the supply chain grows, AI models should be able to handle increased data and computational demands efficiently. It embraces continuing to train the model on a larger dataset or fine-tune it periodically as more data becomes available. Several options exist to deploy models in a production environment, including on-premise deployment, cloud-based services, and edge deployment. The next step is related to integrating AI models with existing supply chain management systems, ERPs, or other relevant software.
Customer acceptance and adoption
Handling the adoption of AI in the supply chain requires a strategic and customer-centric approach. Clear communication, education, customization, and a commitment to continuous improvement are keys to successful adoption. By addressing concerns, providing support, and demonstrating value, businesses know how to build trust and encourage customers to embrace AI technology in supply chain operations. It’s essential to offer customization options to cater to each customer’s specific needs. The team can also collaborate with customers to co-create solutions that align with their goals. That not only fosters acceptance but also strengthens the relationship with customers.
Automation and monitoring
AI implementations should be agile and adaptable to address the changing needs in the supply chain. The establishment of feedback loops enables the continuous improvement of AI models. The team gets the opportunity to monitor the performance and make adjustments as needed. They can implement AI-driven automation for demand forecasting, order fulfillment, inventory management, and predictive maintenance. As a result, it helps optimize processes and reduce manual intervention, ensuring that these AI systems are effectively managed and monitored.
Efficiently adopting AI in supply chain is an ongoing process that requires careful planning, commitment, and adaptability. It’s essential to align adoption with business goals and continuously assess its impact on the supply chain’s performance.
How to start custom supply chain software development from scratch?
Check the comprehensive guide on building supply chain software, its core functionalities, software types, and good practices for covering business-specific requirements.
CONCLUSION
Embracing AI in supply chain is not just a trend but a strategic approach for companies looking to thrive in an increasingly dynamic and complex global marketplace. It is a journey that won’t be completed without planning, investment, and collaboration. But the rewards in terms of efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction are substantial.
Looking for a professional team with first-hand AI experience?
Existek’s team will gladly share our technical expertise and deliver AI-powered solutions to address business needs.
Frequently asked questions
What is AI in supply chain?
It refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies to improve and optimize numerous aspects of supply chain management, including demand forecasting, inventory management, logistics, and more.
How does AI enhance supply chain optimization?
Artificial intelligence is helpful for the optimization of the following areas:
- Demand forecasting
- Inventory management
- Supplier selection and management
- Route optimization
- Warehouse management
- Quality control
- Real-time visibility
- Cost reduction
- Sustainability and compliance
- Customer service and satisfaction
What are the challenges of AI in supply chain?
The major challenges are related to
- Data quality
- Data consistency and integration
- Integration with legacy systems
- Data security
- Scalability opportunities
- Ethical concerns
How to adopt AI in supply chain?
Like with any AI implementation, the process has to undergo the following lifecycle:
- Business problem identification
- Data discovery and preparation
- Model training and validation
- Model scaling and deployment
- Customer acceptance and adoption
- Automation and monitoring