Introduction
Last week, Darktrace detected a targeted Sodinokibi ransomware attack during a 4-week trial with a mid-sized company.
This blog post will go through every stage of the attack lifecycle and detail the attacker’s techniques, tools and procedures used, and how Darktrace detected the attack.
The Sodinokibi group is an innovative threat-actor that is sometimes referred to as a ‘double-threat’, due to their ability to run targeted attacks using ransomware while simultaneously exfiltrating their victim’s data. This enables them to threaten to make the victim’s data publicly available if the ransom is not paid.
While Darktrace’s AI was able to identify the attack in real time as it was emerging, unfortunately the security team didn’t have eyes on the technology and was unable to action the alerts — nor was Antigena set in active mode, which would have slowed down and contained the threat instantaneously.
Timeline
The timeline below provides a rough overview of the major attack phases. Most of the attack took place over the course of a week, with the majority of activity distributed over the last three days.

Technical analysis
Darktrace detected two main devices being hit by the attack: an internet-facing RDP server (‘RDP server’) and a Domain Controller (‘DC’), that also acts as a SMB file server.
In previous attacks, Sodinokibi has used host-level encryption for ransomware activity where the encryption takes place on the compromised host itself — in contrast to network-level encryption where the bulk of the ransomware activity takes place over network protocols such as SMB.
Initial compromise
Over several days, the victim’s external-facing RDP server was receiving successful RDP connections from a rare external IP address located in Ukraine.
Shortly before the initial reconnaissance started, Darktrace saw another RDP connection coming into the RDP server with the same RDP account as seen before. This connection lasted for almost an hour.
It is highly likely that the RDP credential used in this attack had been compromised prior to the attack, either via common brute-force methods, credential stuffing attacks, or phishing.
Thanks to Darktrace’s Deep-Packet Inspection, we can clearly see the connection and all related information.
Suspicious RDP connection information:
Time: 2020-02-10 16:57:06 UTC
Source: 46.150.70[.]86 (Ukraine)
Destination: 192.168.X.X
Destination Port: 64347
Protocol: RDP
Cookie: [REDACTED]
Duration: 00h41m40s
Data out: 8.44 MB
Data in: 1.86 MB
Darktrace detects incoming RDP connections from IP addresses that usually do not connect to the organization.
Attack tools download
Approximately 45 minutes after the suspicious RDP connection from Ukraine, the RDP server connected to the popular file sharing platform, Megaupload, and downloaded close to 300MB from there.
Darktrace’s AI recognized that neither this server, nor its automatically detected peer group, nor, in fact, anyone else on the network commonly utilized Megaupload — and therefore instantly detected this as anomalous behavior, and flagged it as unusual.

As well as the full hostname and actual IP used for the download, Megaupload is 100% rare for this organization.
Later on, we will see over 40GB being uploaded to Megaupload. This initial download of 300MB however is likely additional tooling and C2 implants downloaded by the threat-actor into the victim’s environment.
Internal reconnaissance
Only 3 minutes after the download from Megaupload onto the RDP server, Darktrace alerted on the RDP server doing an anomalous network scan:

The RDP server scanned 9 other internal devices on the same subnet on 7 unique ports: 21, 80, 139, 445, 3389, 4899, 8080 . Anybody with some offensive security know-how will recognize most of these ports as default ports one would scan for in a Windows environment for lateral movement. Since this RDP server does not usually conduct network scans, Darktrace again identified this activity as highly anomalous.
Later on, we see the threat-actor do more network scanning. They become bolder and use more generic scans — one of them showing that they are using Nmap with a default user agent:

Additional Command and Control traffic
While the initial Command and Control traffic was most likely using predominantly RDP, the threat-actor now wanted to establish more persistence and create more resilient channels for C2.
Shortly after concluding the initial network scans (ca. 19:17 on 10th February 2020), the RDP server starts communicating with unusual external services that are unique and unusual for the victim’s environment.
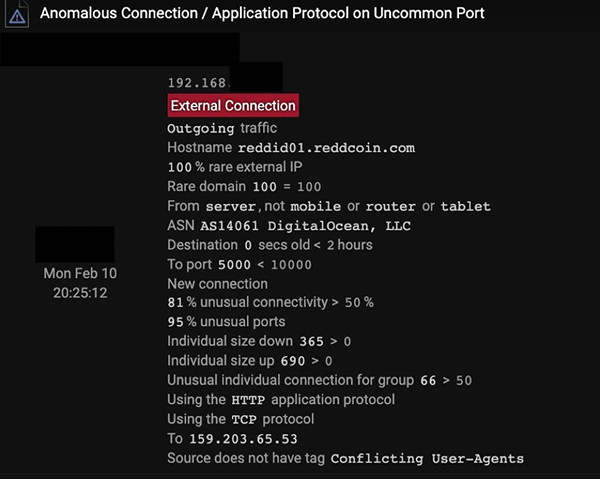
Communications to Reddcoin
Again, nobody else is using Reddcoin on the network. The combination of application protocol and external port is extremely unusual for the network as well.
The communications also went to the Reddcoin API, indicating the installation of a software agent rather than manual communications. This was detected as Reddcoin was not only rare for the network, but also ‘young’ — i.e. this particular external destination had never been seen to be contacted before on the network until 25 minutes before.

Communications to the Reddcoin API

Communications to Exceptionless[.]io
As we can see, the communications to exceptionalness[.]io were done in a beaconing manner, using a Let’s Encrypt certificate, being rare for the network and using an unusual JA3 client hash. All of this indicates the presence of new software on the device, shortly after the threat-actor downloaded their 300MB of tooling.
While most of the above network activity started directly after the threat-actor dropped their tooling on the RDP server, the exact purpose of interfacing with Reddcoin and Exceptionless is unclear. The attacker seems to favor off-the-shelf tooling (Megaupload, Nmap, …) so they might use these services for C2 or telemetry-gathering purposes.
This concluded most of the activity on February 10.
More Command and Control traffic
Why would an attacker do this? Surely using all this C2 at the same time is much noisier than just using 1 or 2 channels?
Another significant burst of activity was observed on February 12 and 13.
The RDP server started making a lot of highly anomalous and rare connections to external destinations. It is inconclusive if all of the below services, IPs, and domains were used for C2 purposes only, but they are linked with high-confidence to the attacker’s activities:
- HTTP beaconing to vkmuz[.]net
- Significant amount of Tor usage
- RDP connections to 198-0-244-153-static.hfc.comcastbusiness[.]net over non-standard RDP port 29348
- RDP connections to 92.119.160[.]60 using an administrative account (geo-located in Russia)
- Continued connections to Megaupload
- Continued SSL beaconing to Exceptionless[.]io
- Continued connections to api.reddcoin[.]com
- SSL beaconing to freevpn[.]zone
- HTTP beaconing to 31.41.116[.]201 to /index.php using a new User Agent
- Unusual SSL connections to aj1713[.]online
- Connections to Pastebin
- SSL beaconing to www.itjx3no[.]com using an unusual JA3 client hash
- SSL beaconing to safe-proxy[.]com
- SSL connection to westchange[.]top without prior DNS hostname lookups (likely machine-driven)
What is significant here is the diversity in (potential) C2 channels: Tor, RDP going to dynamic ISP addresses, VPN solutions and possibly custom / customized off-the-shelf implants (the DGA-looking domains and HTTP to IP addresses to /index.php).
Why would an attacker do this? Surely using all this C2 at the same time is much noisier than just using 1 or 2 channels?
One answer might be that the attacker cared much more about short-term resilience than about stealth. As the overall attack in the network took less than 7 days, with a majority of the activity taking place over 2.5 days, this makes sense. Another possibility might be that various individuals were involved in parallel during this attack — maybe one attacker prefers the comfort of RDP sessions for hacking while another is more skilled and uses a particular post-exploitation framework.
The overall modus operandi in this financially-motivated attack is much more smash-and-grab than in the stealthy, espionage-related incidents observed in Advanced Persistent Threat campaigns (APT).
Data exfiltration
The DC uploaded around 40GB of data to Megaupload over the course of 24 hours.
While all of the above activity was seen on the RDP server (acting as the initial beach-head), the following data exfiltration activity was observed on a Domain Controller (DC) on the same subnet as the RDP server.
The DC uploaded around 40GB of data to Megaupload over the course of 24 hours.
Darktrace detected this data exfiltration while it was in progress — never did the DC (or any similar devices) upload similar amounts of data to the internet. Neither did any client nor server in the victim’s environment use Megaupload:

Ransom notes
Finally, Darktrace observed unusual files being accessed on internal SMB shares on February 13. These files appear to be ransom notes — they follow a similar, randomly-generated naming convention as other victims of the Sodinokibi group have reported:
413x0h8l-readme.txt
4omxa93-readme.txt
Conclusion and observations
The threat-actor seems to be using mostly off-the-shelf tooling which makes attribution harder — while also making detection more difficult.
This attack is representative of many of the current ransomware attacks: financially motivated, fast-acting, and targeted.
The threat-actor seems to be using mostly off-the-shelf tooling (RDP, Nmap, Mega, VPN solutions) which makes attribution harder — while also making detection more difficult. Using this kind of tooling often allows to blend in with regular admin activity — only once anomaly detection is used can this kind of activity be detected.
How can you spot the one anomalous outbound RDP connection amongst the thousands of regular RDP connections leaving your environment? How do you know when the use of Megaupload is malicious — compared to your users’ normal use of it? This is where the power of Darktrace’s self-learning AI comes into play.
Darktrace detected every stage of the visible attack lifecycle without using any threat intelligence or any static signatures.
The graphics below show an overview of detections on both compromised devices. The compromised devices were the highest-scoring assets for the network — even a level 1 analyst with limited previous exposure to Darktrace could detect such an in-progress attack in real time.

RDP Server
Some of the detections on the RDP server include:
- Compliance / File Storage / Mega — using Megaupload in an unusual way
- Device / Network Scan — detecting unusual network scans
- Anomalous Connection / Application Protocol on Uncommon Port — detecting the use of protocols on unusual ports
- Device / New Failed External Connections — detecting unusual failing C2
- Compromise / Unusual Connections to Let’s Encrypt — detecting potential C2 over SSL using Let’s Encrypt
- Compromise / Beacon to Young Endpoint — detecting C2 to new external endpoints for the network
- Device / Attack and Recon Tools — detecting known offensive security tools like Nmap
- Compromise / Tor Usage — detecting unusual Tor usage
- Compromise / SSL Beaconing to Rare Destination — detecting generic SSL C2
- Compromise / HTTP Beaconing to Rare Destination — detecting generic HTTP C2
- Device / Long Agent Connection to New Endpoint — detecting unusual services on a device
- Anomalous Connection / Outbound RDP to Unusual Port — detecting unusual RDP C2

DC
Some of the detections on the DC include:
- Anomalous Activity / Anomalous External Activity from Critical Device — detecting unusual behaviour on dcs
- Compliance / File storage / Mega — using Megaupload in an unusual way
- Anomalous Connection / Data Sent to New External Device — data exfiltration to unusual locations
- Anomalous Connection / Uncommon 1GB Outbound — large amounts of data leaving to unusual destinations
- Anomalous Server Activity / Outgoing from Server — likely C2 to unusual endpoint on the internet