Satellite imagery and machine learning offer a new, far more detailed look at the maritime industry, specifically the number and activities of fishing and transport ships at sea. Turns out there are way more of them than publicly available data would suggest, a fact that policymakers should heed.
As a shared global resource, the oceans are everyone’s business, but of course not every country or region has the same customs, laws or even motivations.
There is the automated identification system (AIS) increasingly adopted around the world that uses shipboard transponders to precisely track activity, but it is far from universal in application. As a result, important data like how many vessels are fishing in an area, who operates them and how much fish they’re taking is often unclear, a patchwork of local, proprietary and government-approved numbers.
Not only does this make policy decisions difficult and approximate, but there is a sense of lawlessness to the industry, with countless ships clandestinely visiting restricted or protected waters or wildly exceeding safe harvesting numbers for quickly depleting stocks.
Satellite imagery offers a new perspective on this conundrum: You can’t hide from an eye in the sky. But the scale of the industry and the imagery documenting it are both immense. Fortunately machine learning is here to perform the millions of vessel recognition and tracking operations necessary to accurately track the tens of thousands of ships at sea at any given moment.
In a paper published in Nature, Fernando Paolo, David Kroodsma and their team at Global Fishing Watch (with collaborators at multiple universities) analyzed two petabytes of orbital imagery from 2017-2021, identifying millions of vessels at sea and cross-referencing them with reported and known coordinates for vessels tracked via AIS.
What the study documents is that around three-fourths of all industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked, and likewise almost a third of all transport and energy vessels. The dark fishing industry is huge — perhaps as big again as the publicly documented one. (The imagery also counted increases in wind turbine and other renewable energy placements, which can be similarly difficult to track.)
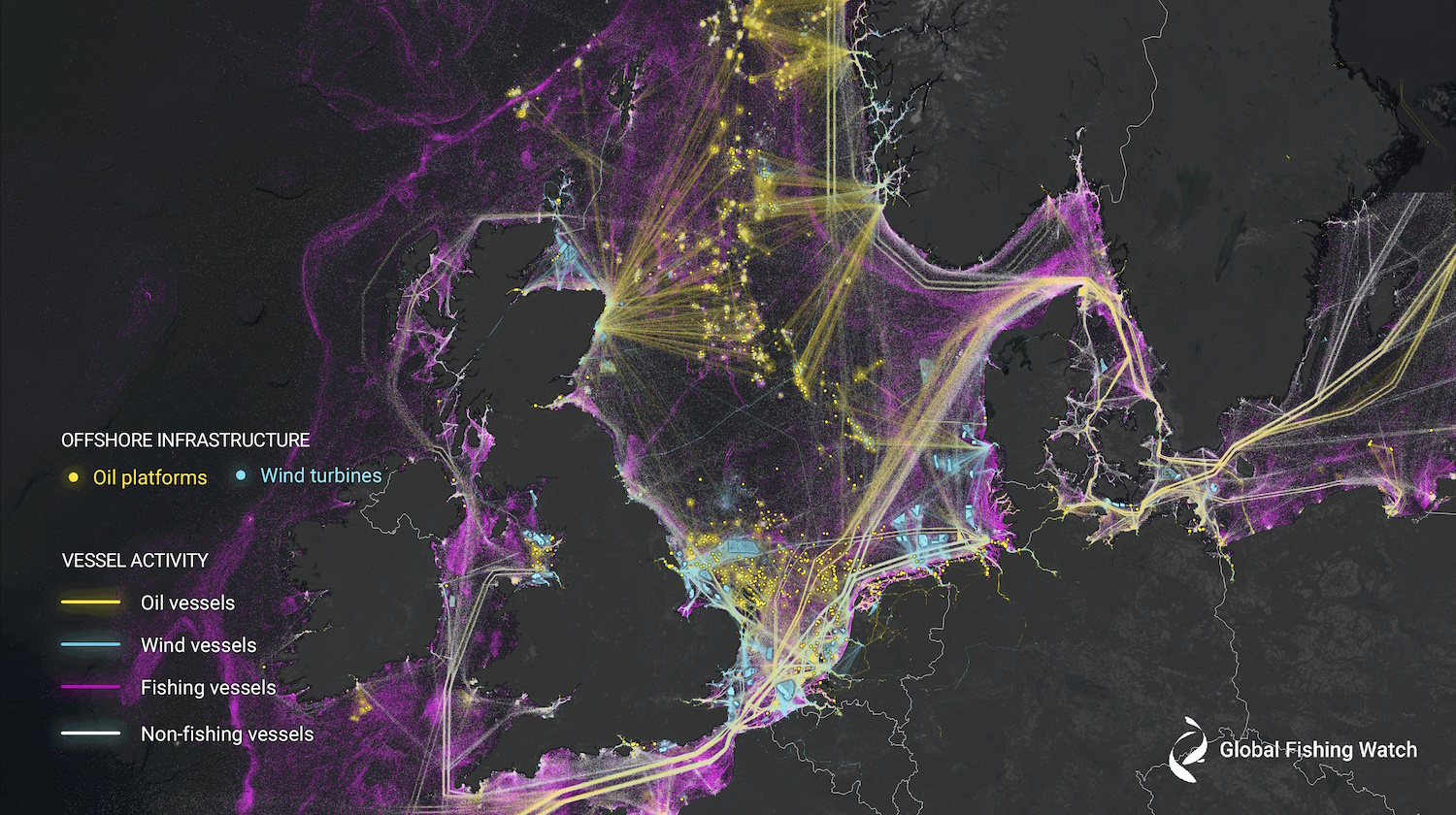
Now, “not publicly tracked” doesn’t mean totally unaccounted for.
“There are a few reasons why these vessels are missing from public tracking systems,” Paolo explained to TechCrunch. For instance, smaller vessels and those operating in areas with little or no satellite coverage or AIS infrastructure are equally “untracked” as ones that deliberately turn off their transponders or otherwise avoid detection.
“It is important to note that some countries have other (proprietary) means to track vessels within their own waters. But these proprietary systems are limited to the vessels they can track and this information is not shared with other nations,” he continued.
As the population grows and the oceans warm, it’s increasingly crucial that data like this is known beyond a nation’s borders and internal agencies.
“Fish are an important dynamic resource that move around, so openly tracking fishing vessels is fundamental for monitoring fish stocks. It is difficult to understand and map the full ecological footprint of vessels without all of them publicly broadcasting their positions and activity,” said Paolo.

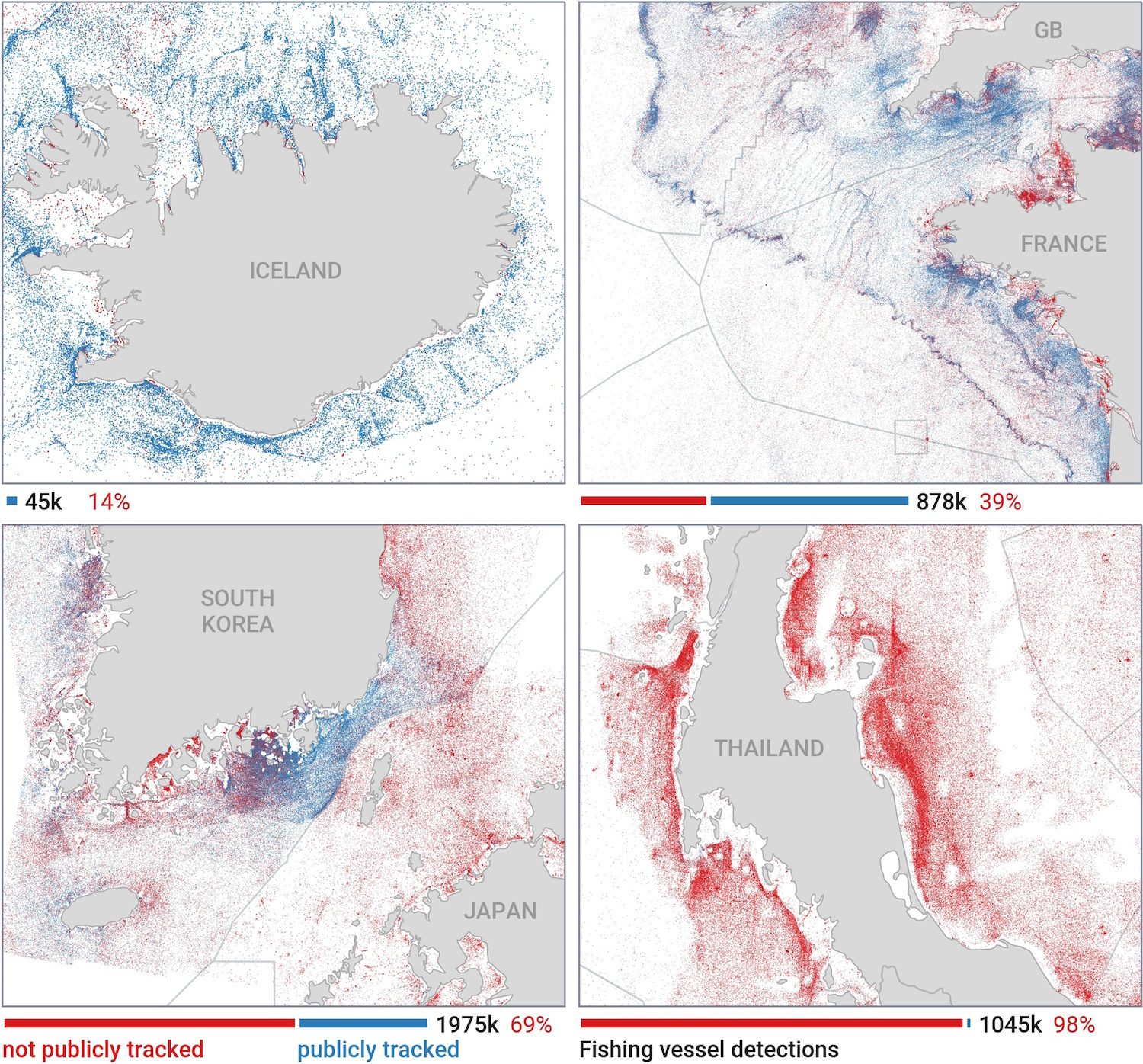
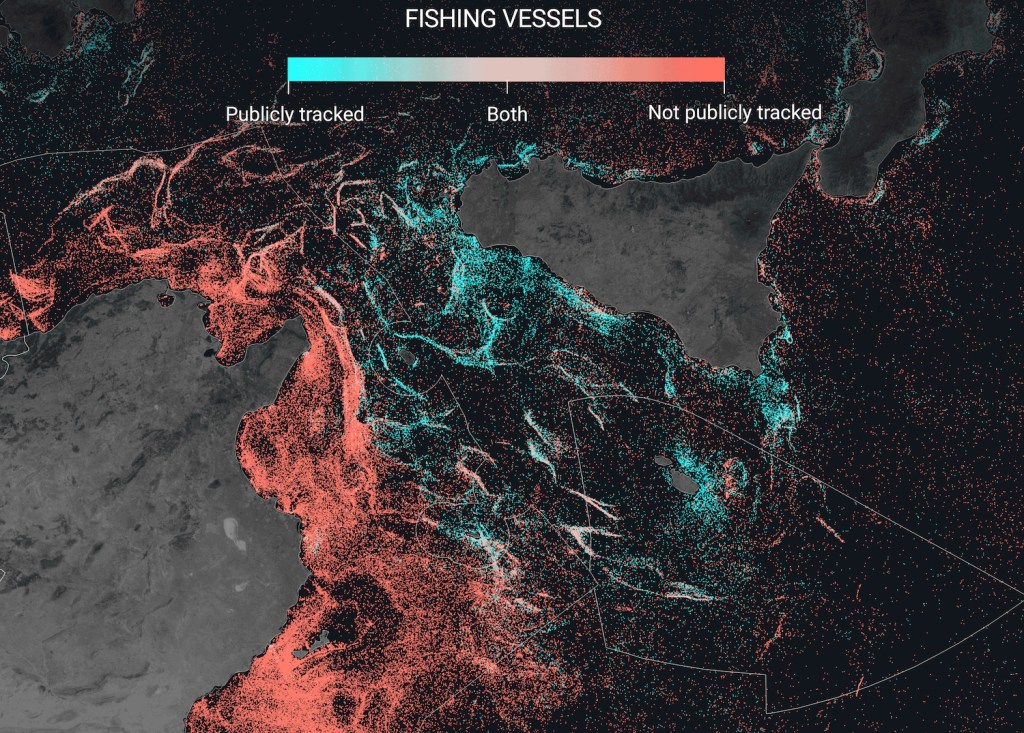
You can see in the visualizations that Iceland and the Nordics have the highest levels of tracking, while Southeast Asia has the lowest — down to practically zero off the coast of Bangladesh, India and Myanmar.
As noted above, this doesn’t mean they’re all illegal, just that their activity is not shared, as is legally required in the Nordics. How much fishing is done by these areas? The global community only hears second-hand, and one of the study’s findings was that the Asian fishing industry is systematically under-represented.
If you were to count based on AIS data, you’d find that about 36% of fishing activity was in European waters, and 44% in Asia. But the satellite data completely contradicts this, showing that only 10% of fishing vessels are in European waters, and a staggering 71% in Asian waters. In fact, China alone appears to account for some 30% of all fishing on the planet!
This is not meant to blame or fault those countries or regions, but simply to point out that our understanding of the scale of the global fishing industry is all wrong. And if we don’t have good information to base our policies and science on, both will end up fundamentally flawed.
That said, the satellite analysis also showed the regular presence of fishing boats in protected areas like the Galapagos Islands, which is strictly forbidden by international law. You can bet those dark vessels got a little extra attention.
“The next step is to work with authorities in different regions to assess these new maps. In some cases we have likely found some fishing within marine protected areas or restricted areas that will require further investigation and protection,” Paolo said.
He hopes that improved data will help guide policy, but the gathering and analysis is far from complete.
“This is only the first version of our open data platform,” he said. “We are processing new radar imagery from the Sentinel-1 satellite as it is collected and identifying activity across the globe. This data can be seen and accessed on our website, globalfishingwatch.org, and is current up to three days ago.”
The nonprofit organization is supported by a number of philanthropies and individuals, which you can find listed here.






























Comment