Smartphone cameras have gotten quite good, but it’s getting harder and harder to improve them because we’ve pretty much reached the limit of what’s possible in the space of a cubic centimeter. Glass is a startup looking to fundamentally change how the camera works, using a much bigger sensor and an optical trick from the depths of filmmaking: anamorphic lenses.
It may not be obvious that cameras won’t get better, since we’ve seen such advances in recent generations of phones. But we’ve used up all the slack left in this line, as it were.
To improve the image, you need a bigger sensor, better lens or some kind of computational wizardry. Unfortunately, sensors can’t get much bigger because they’d need bigger lenses to match. And lenses can’t get bigger because there’s just no room for them in the phone body, even when you “fold” the camera. Meanwhile, computational photography is great, but there’s only so much it can do — stacking a few images to get better dynamic range or depth information is good, but you reach a point of diminishing returns pretty quickly.
“The limitations used to be about price, but now it’s size,” explained Glass co-founder and CEO Ziv Attar, who has worked in mobile imaging for over a decade, including at Apple. The other co-founder, Tom Bishop, also worked at Apple, the two of them working on creating Portrait Mode and likely chafing at the limitations of traditional camera design.
“Up to 5 years ago they just made the lens wider, then they started making the sensor bigger,” Attar said. “Then you throw algorithms at it to reduce noise, but even that is reaching its limits; pretty soon it will be pure hallucination [i.e. AI-generated imagery]. Night mode takes exposure stacking to extremes — it deals very nicely with the lack of photons, but if you zoom in it starts to look very weird and fake.”
“The phone screen kind of deceives us,” he continued. “If you let a regular person compare an iPhone 12 and 13, they won’t see the difference — but compared to a pro camera, anyone can tell. And if you can see the difference, there’s a lot of work to do.”
So what is that work, exactly? Attar has decided that of these various conundrums, the only one that makes sense to change is the lens. True, it can’t get any bigger — but only if you’re using a normal, symmetrical lens assembly. But why should we? They gave up on that constraint a century ago in cinema.
Anamorphic evolution

Films weren’t always widescreen. Originally they were more likely to be approximately the shape of a 35mm film frame, for obvious reasons. If you matted out the top and bottom, you could project a widescreen image, which people liked — but you were basically just zooming in on a part of the film, which you paid for in detail. But a technique first tested in the ’20s soon solved the problem.
Anamorphic lenses squeeze a wide field of view from the sides so it fits in the film frame, and when projected using an anamorphic projector, the process was reversed — the image is stretched back out to the desired aspect ratio. There are a few interesting optical effects introduced but… if I describe them you’ll never be able to un-see them in content, so I’ll forbear.
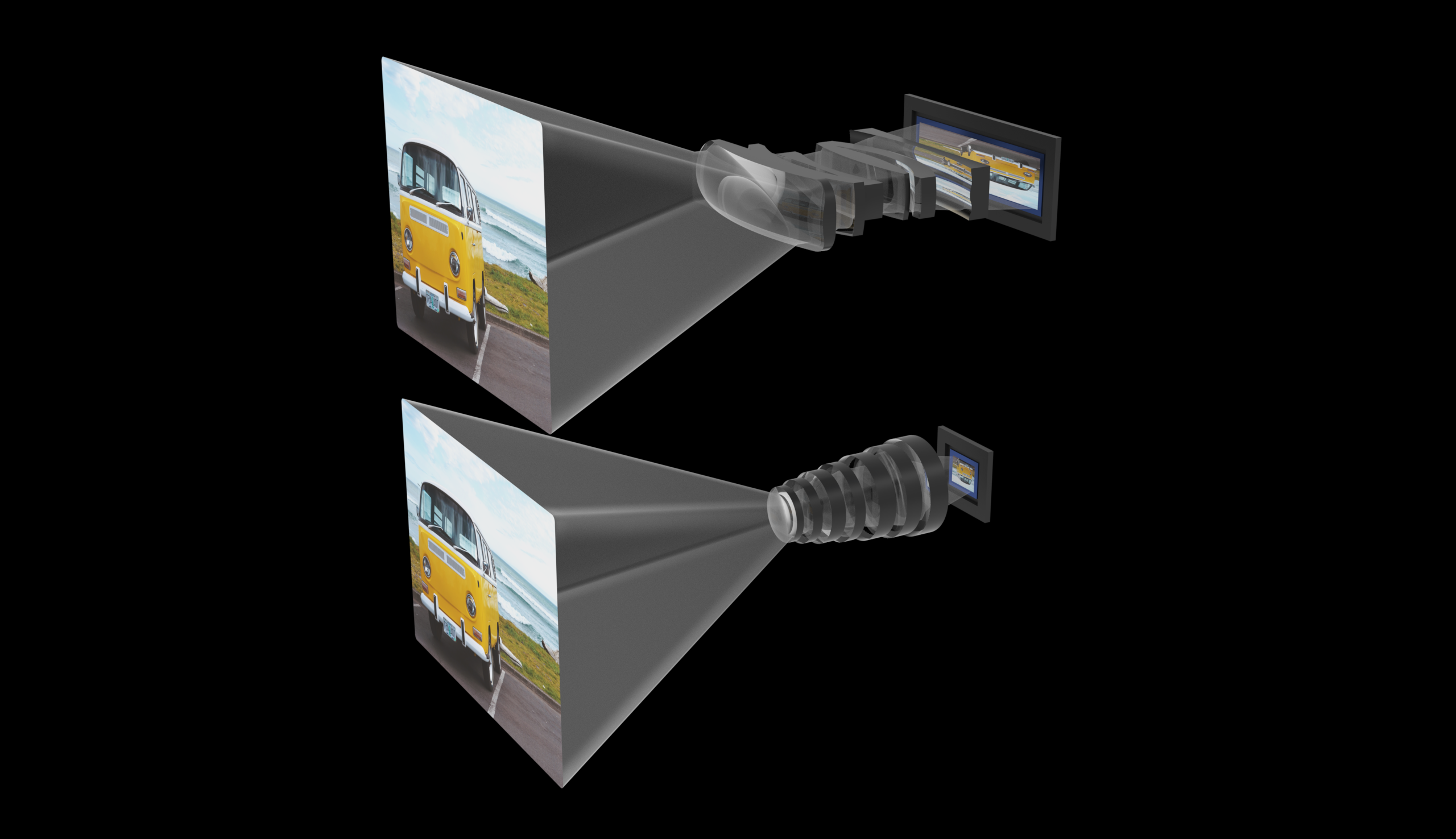
The lens system proposed by Glass isn’t quite the same, but it uses similar principles and unusually shaped lenses. It started from the fundamental idea of how to add a larger sensor. Simply making a larger square would necessitate a larger lens, which we can’t do — but what if you made the sensor longer, as in a rectangle? Well, you’d need a longer, rectangular lens too. The anamorphic technique means you can capture and project a larger but distorted image, then convert it to the right aspect ratio in the image processor. (The process isn’t exactly analogous to the film technique but it uses the same principles.)
How much larger an image are you able to capture? Well, an iPhone 13’s main camera has a sensor about 7×5 millimeters, so 35 square mm total. Glass’s prototype uses a sensor that’s about 24×8 mm: about 192 square mm, 5-6 times larger, with a commensurate increase to megapixels. Here’s a little chart for casual reference:

Considering the fanfare that generally accompanies increasing a phone’s sensor size by 15 or 20 percent, that’s an enormous leap.
But Attar explained that the way they measure it, it’s even more. If you were to expand the image to the correct aspect ratio, it would actually be twice as tall: 24x16mm, just shy of the APS-C standard in DSLRs but well above the Micro Four Thirds and 1″ sensors also common (and highly performant) in mirrorless cameras. That leads to the company’s claim of having 11 times the “imaging area” of an iPhone. The evaluation of these metrics is a non-trivial process I’m not equipped to do, but truthfully either one would be a game-changing upgrade for a phone.
Bigger, brighter and a bit weirder
There are benefits and drawbacks to this process. The most important one is an immense increase in light gathering and resolving power. More light means better exposures in general and better shots in challenging conditions — no need for a fancy machine learning powered multi-exposure night mode if you can just… see things. And there is far, far more detail in images compared with those from ordinary smartphones.
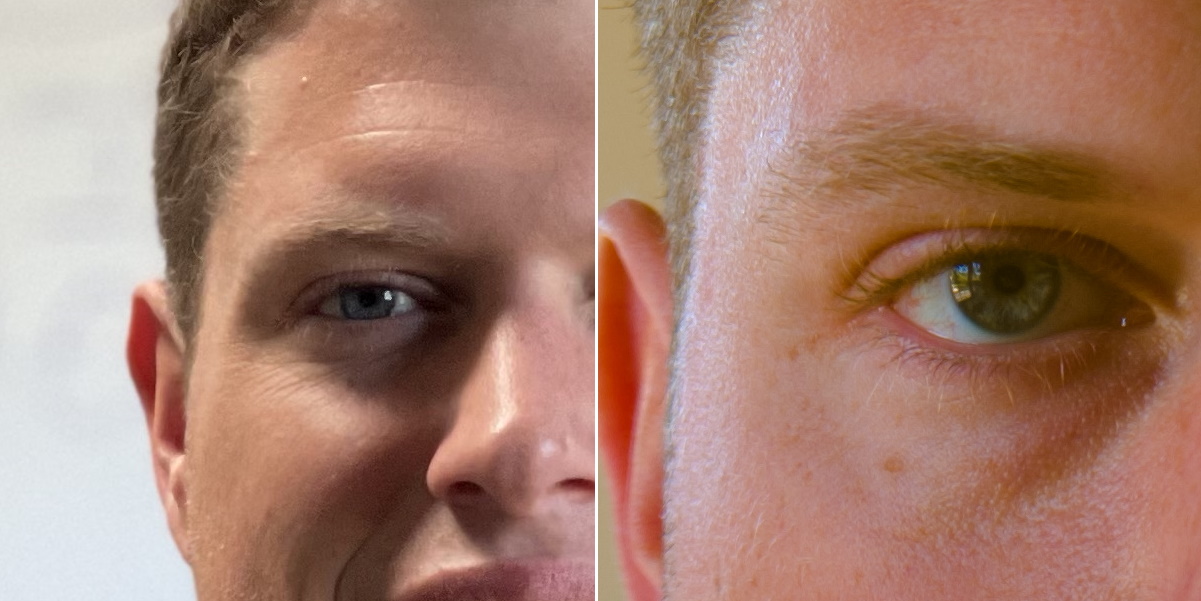

Note that the limited example above is just that — it’s hard to do apples-to-apples comparisons when the focal lengths, image processing and output resolution are so different (not to mention my cropping and re-encoding), but at the very least you can see that a great deal of detail is added even in this non-optimal presentation. The full-size original images are available here: iPhone, Glass.
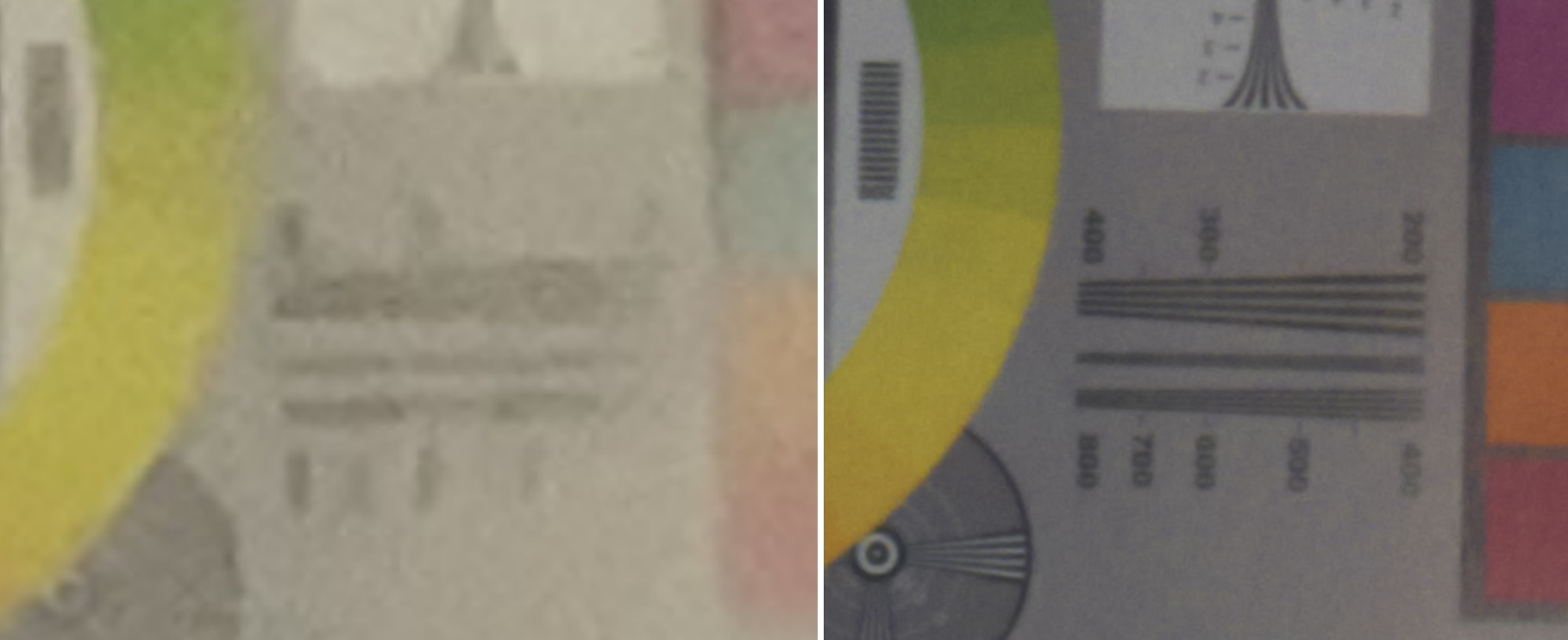

Because of the larger sensor and the nature of the glass, you also get natural bokeh, or background blur. Portrait mode is of course a favorite among smartphone users, but even the best methods of simulating bokeh are far from perfect. The same effect Apple painstakingly simulated lenses to achieve occurs naturally on the Glass prototype, just as it would on a larger digital camera. And there’s no chance of the kind of weird mistake you see in the AI-segmented images, which often clip out hair and other details, or fail to achieve the depth effect in subtler ways.
While there would be no optical zoom, Attar pointed out that zooming in by cropping (i.e. digital zoom) on a Glass system would let you zoom in more than most optical zooms out there, and you’d still have more light and pixels than the competition. I’m not normally one to let “digital zoom is fine” claims live, but in this case the sheer size of the lens and sensor more than make up for it.
These benefits, though briefly stated, are more than considerable. The improvement to light and detail puts it way out in front of the best cameras out there. (And while the smallest details may escape your notice on a small screen, a bad exposure is noticeable at any size.)
Drawbacks are mainly to do with the complexities of operating a camera that’s totally optically different from a traditional one. The mechanisms for autofocus are different (anamorphic focus is notoriously complex) and there are plenty of distortions and aberrations that need to be corrected for — symmetrical lenses at this size also have distortion and degradation, but of a different type.
“[Distortions] are all constrained during design such that we know in advance that we can correct for them,” said Attar. “It’s an iterative process but we did kick start development of a custom dedicated software tool to co-optimize lens parameters and neural network variables.” In other words they didn’t design anything they couldn’t correct for.
One effect I find disorientating but perhaps others will decide is trivial is the shape of the bokeh. Normally out of focus highlights blur out into little translucent discs, but in the Glass system they resolve into a gradient of ovals and chubby crescents.
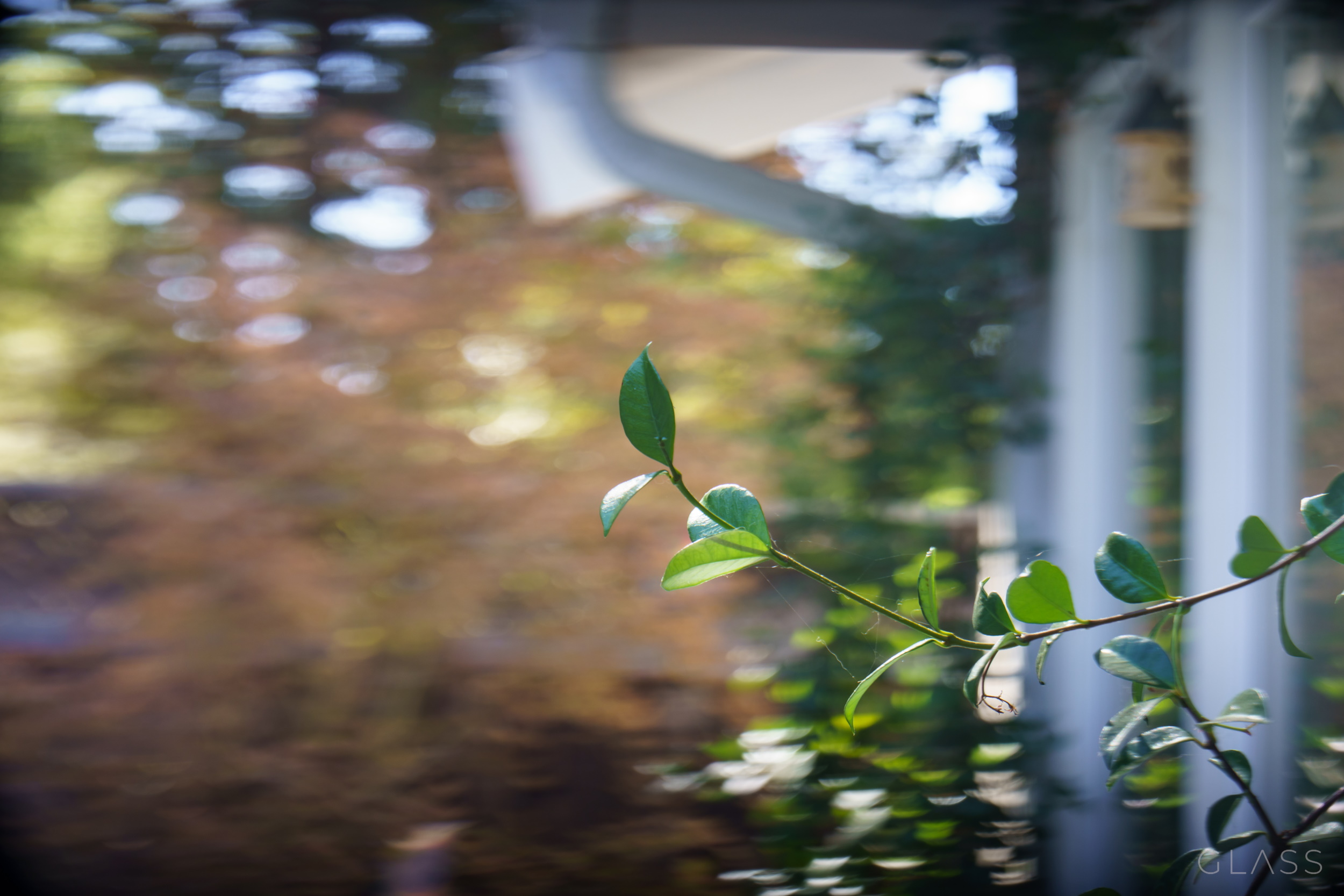

To my neurotic eye that just isn’t right. It’s… unnatural. But I also can’t not notice vignetted bokeh due to french flags in film and TV (don’t look it it up — this too is everywhere and you can’t unsee it). And anyway films shot in anamorphic show similar bokeh distortion, so it’s actually quite common, just not in still images and smartphone shots.
I assumed there would be drawbacks due to the need to stretch the image digitally — that sort of thing if done poorly can lead to moiré and other unwanted artifacts. But Attar said it’s remarkably straightforward to train a model to do it so that no one can tell the difference except pixel peepers: “We trained networks to apply 1-D super-resolution based on information from the other axes. After we apply our algorithm it looks like it came from a full APS-C sensor, in field of view and resolution.”
That will all have to be verified by reviewers and camera experts when there’s a production version, but the theory seems sound and the early results are more than promising.
Right now the company has moved on from standalone prototypes to a third-generation phone factor device that shows how the tech will fit into pretty much any chassis on the market. There’s nothing exotic about it other than the optical qualities, Attar said, so although it won’t be as cheap to manufacture as today’s off-the-shelf camera and image processing units, it can be made just as easily. As he noted, price is hardly an option any more, and if one company can make a huge leap in camera quality they can capture a large chunk of the market.
“We have to convince a phone maker to basically ditch the old technology,” said Attar. “We’re seeing nice feedback. The only challenge is doing it in a reasonable time. I’m not saying there’s no risk. But a lot of us had good jobs at big companies — we didn’t leave our fancy salaries at Apple to work on some BS thing. We had a plan from the beginning.”
Even if an agreement was struck now with a big mobile manufacturer, it would take a year and half or two years to get to market. “But we have to start somewhere,” he concluded.
Glass has raised $2.2 million in seed funding, led by LDV Capital and a collection of angel investors. Of course that’s not meant to cover the cost of manufacturing, but now that the company is leaving the lab it will need operating cash to commercialize even should a major manufacturer make a commitment. Greg Gilley, formerly Apple’s VP of cameras and photos, and MIT Media lab’s Ramesh Raskar joined as advisors, rounding out a team investors are likely to have a lot of confidence in.
If the Glass approach catches on, expect to hear about other companies claiming to have invented it in a little less than two years.































Comment