Heartex, a startup that bills itself as an “open source” platform for data labeling, today announced that it landed $25 million in a Series A funding round led by Redpoint Ventures. Unusual Ventures, Bow Capital and Swift Ventures also participated, bringing Heartex’s total capital raised to $30 million.
Co-founder and CEO Michael Malyuk said that the new money will be put toward improving Heartex’s product and expanding the size of the company’s workforce from 28 people to 68 by the end of the year.
“Coming from engineering and machine learning backgrounds, [Heartex’s founding team] knew what value machine learning and AI can bring to the organization,” Malyuk told TechCrunch via email. “At the time, we all worked at different companies and in different industries yet shared the same struggle with model accuracy due to poor-quality training data. We agreed that the only viable solution was to have internal teams with domain expertise be responsible for annotating and curating training data. Who can provide the best results other than your own experts?”
Software developers Malyuk, Maxim Tkachenko and Nikolay Lyubimov co-founded Heartex in 2019. Lyubimov was a senior engineer at Huawei before moving to Yandex, where he worked as a backend developer on speech technologies and dialogue systems.
The ties to Yandex, a company sometimes referred to as the “Google of Russia”, might unnerve some — particularly in light of accusations by the European Union that Yandex’s news division played a sizeable role in spreading Kremlin propaganda. Heartex has an office in San Francisco, California, but several of the company’s engineers are based in the former Soviet Republic of Georgia.
When asked, Heartex says that it doesn’t collect any customer data and open sources the core of its labeling platform for inspection. “We’ve built a data architecture that keeps data private on the customer’s storage, separating the data plane and control plane,” Malyuk added. “Regarding the team and their locations, we’re a very international team with no current members based in Russia.”
Setting aside its geopolitical affiliations, Heartex aims to tackle what Malyuk sees as a major hurdle in the enterprise: extracting value from data by leveraging AI. There’s a growing wave of businesses aiming to become “data-centric” — Gartner recently reported that enterprise use of AI grew a whopping 270% over the past several years. But many organizations are struggling to use AI to its fullest.
“Having reached a point of diminishing returns in algorithm-specific development, enterprises are investing in perfecting data labeling as part of their strategic, data-centric initiatives,” Malyuk said. “This is a progression from earlier development practices that focused almost exclusively on algorithm development and tuning.”
If, as Malyuk asserts, data labeling is receiving increased attention from companies pursuing AI, it’s because labeling is a core part of the AI development process. Many AI systems “learn” to make sense of images, videos, text and audio from examples that have been labeled by teams of human annotators. The labels enable the systems to extrapolate the relationships between the examples (e.g. the link between the caption “kitchen sink” and a photo of a kitchen sink) to data the systems haven’t seen before (e.g. photos of kitchen sinks that weren’t included in the data used to “teach” the model).
The trouble is, not all labels are created equal. Labeling data like legal contracts, medical images and scientific literature requires domain expertise that not just any annotator has. And — being human — annotators make mistakes. In an MIT analysis of popular AI datasets, researchers found mislabeled data like one breed of dog confused for another and an Ariana Grande high note categorized as a whistle.
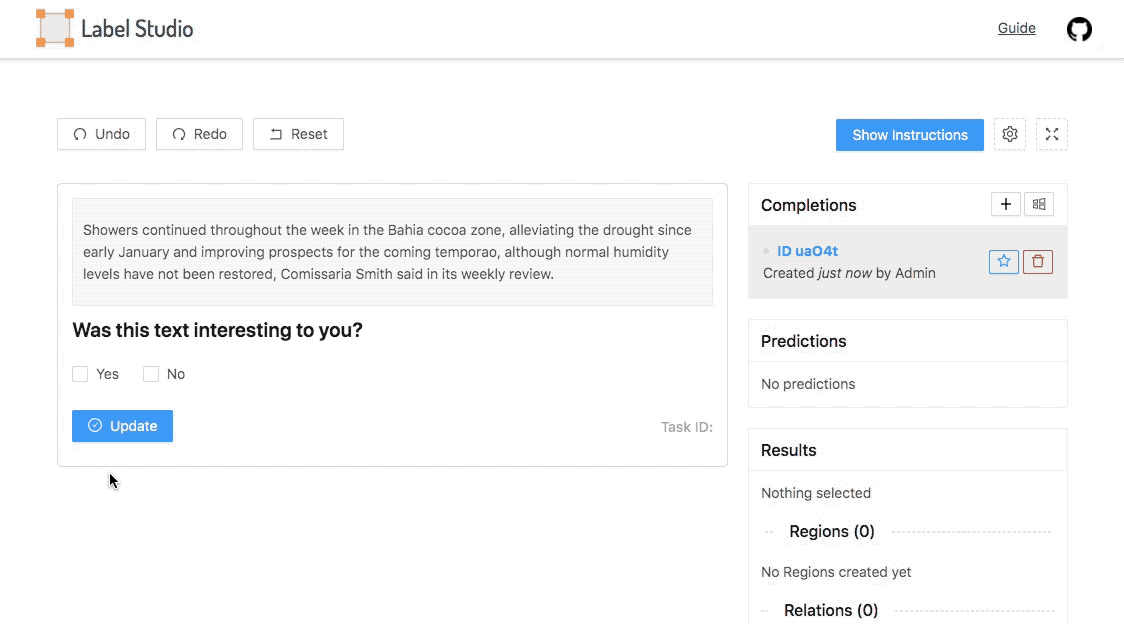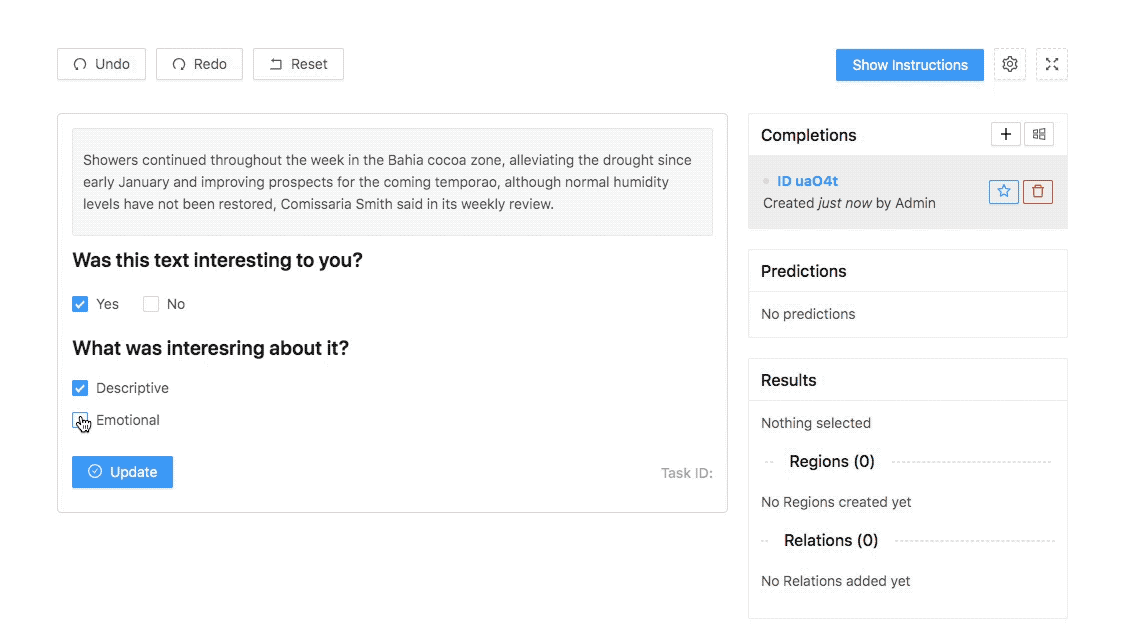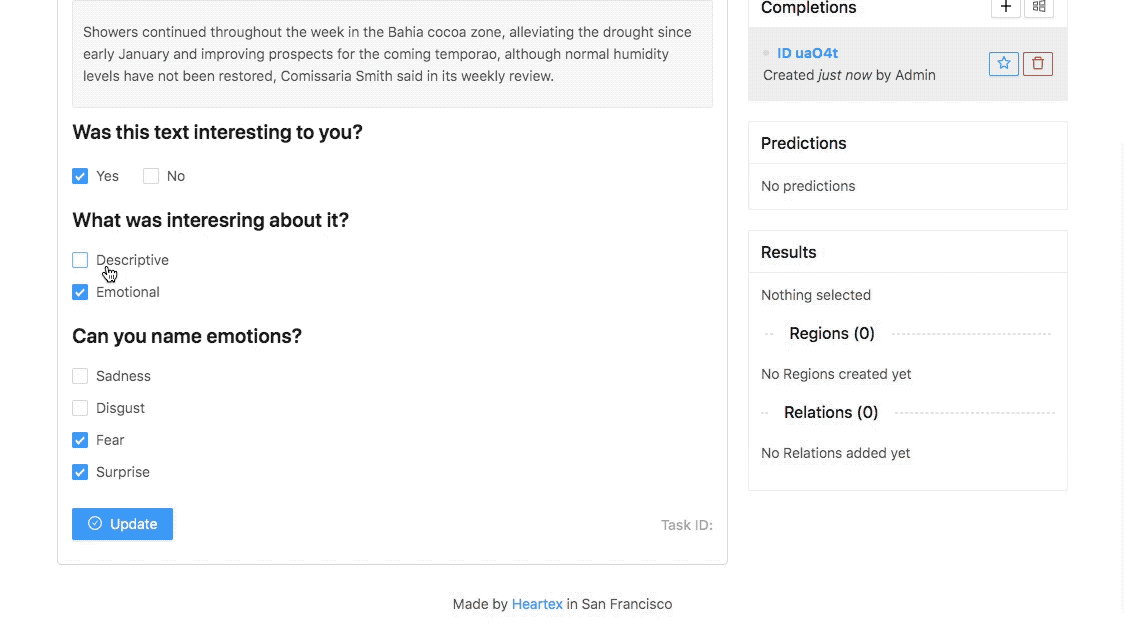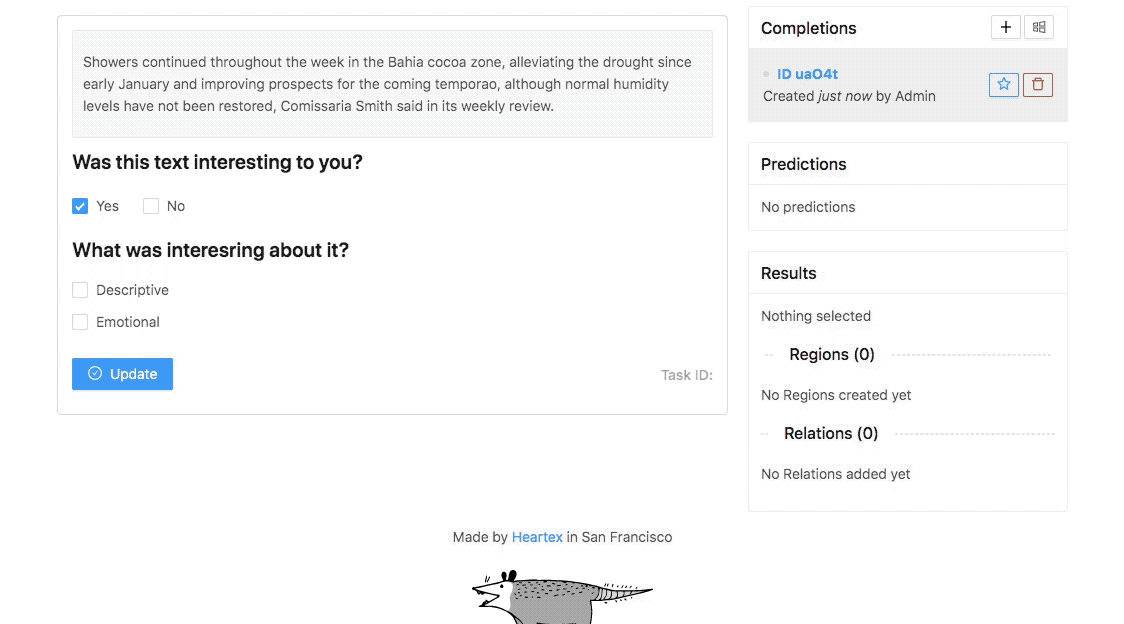
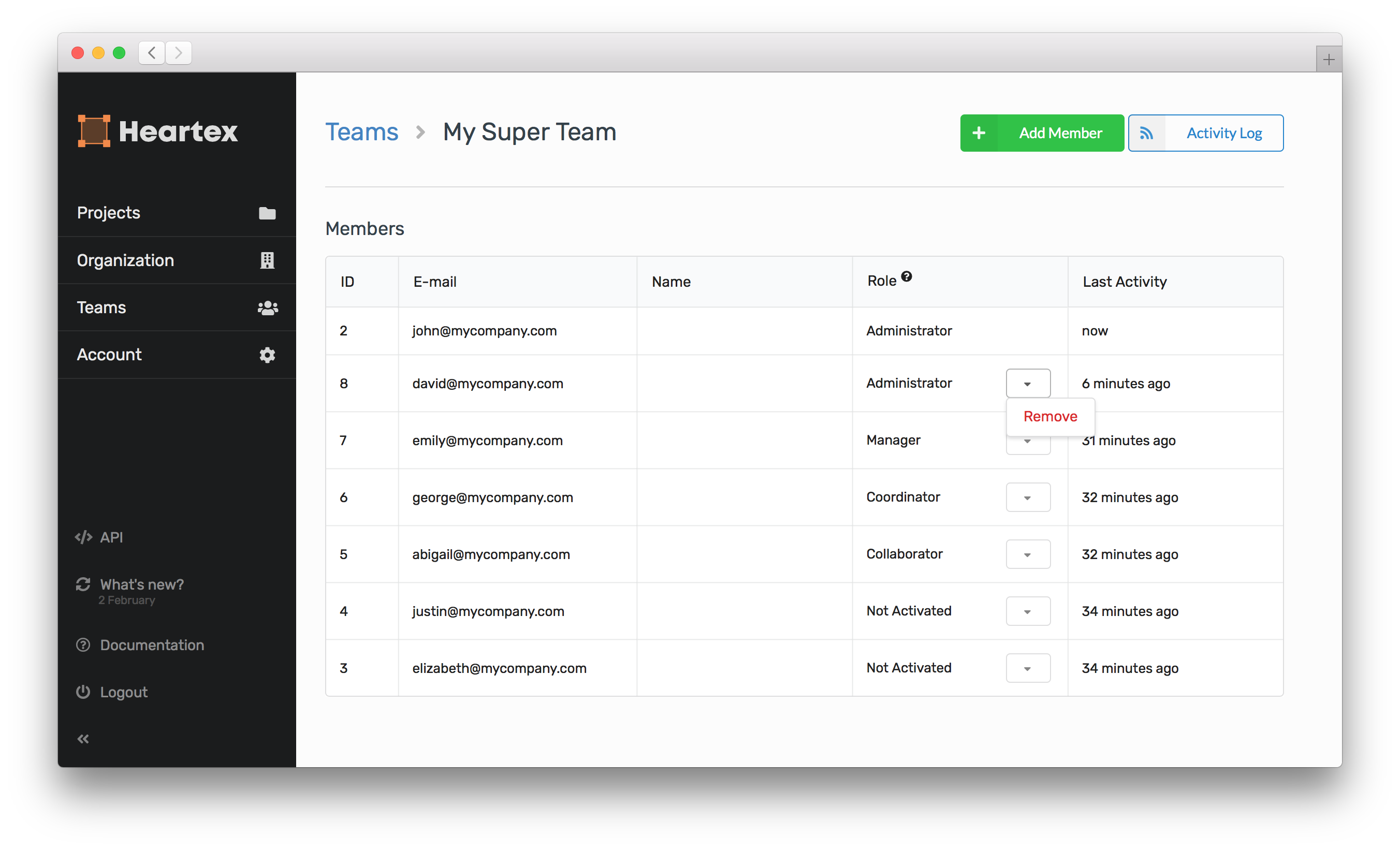
Malyuk makes no claim that Heartex completely solves these issues. But in an interview, he explained that the platform is designed to support labeling workflows for different AI use cases, with features that touch on data quality management, reporting and analytics. For example, data engineers using Heartex can see the names and email addresses of annotators and data reviewers, which are tied to labels that they’ve contributed or audited. This helps to monitor label quality and — ideally — to fix problems before they impact training data.
“The angle for the C-suite is pretty simple. It’s all about improving production AI model accuracy in service of achieving the project’s business objective,” Malyuk said. “We’re finding that most C-suite managers with AI, machine learning, and/or data science responsibilities have confirmed through experience that, with more strategic investments in people, processes, technology, and data, AI can deliver extraordinary value to the business across a multitude of diverse use cases. We also see that success has a snowball effect. Teams that find success early are able to create additional high-value models more quickly building not just on their early learnings but also on the additional data generated from using the production models.”
In the data labeling toolset arena, Heartex competes with startups including AIMMO, Labelbox, Scale AI and Snorkel AI, as well as Google and Amazon (which offers data labeling products through Google Cloud and SageMaker, respectively). But Malyuk believes that Heartex’s focus on software as opposed to services sets it apart from the rest. Unlike many of its competitors, the startup doesn’t sell labeling services through its platform.
“As we’ve built a truly horizontal solution, our customers come from a variety of industries. We have small startups as customers, as well as several Fortune 100 companies. [Our platform] has been adopted by over 100,000 data scientists globally,” Malyuk said, while declining to reveal revenue numbers. “[Our customers] are establishing internal data annotation teams and buying [our product] because their production AI models aren’t performing well and recognize that poor training data quality is the primary cause.”































Comment