There’s more AI news out there than anyone can possibly keep up with. But you can stay tolerably up to date on the most interesting developments with this column, which collects AI and machine learning advancements from around the world and explains why they might be important to tech, startups or civilization.
To begin on a lighthearted note: The ways researchers find to apply machine learning to the arts are always interesting — though not always practical. A team from the University of Washington wanted to see if a computer vision system could learn to tell what is being played on a piano just from an overhead view of the keys and the player’s hands.
Audeo, the system trained by Eli Shlizerman, Kun Su and Xiulong Liu, watches video of piano playing and first extracts a piano-roll-like simple sequence of key presses. Then it adds expression in the form of length and strength of the presses, and lastly polishes it up for input into a MIDI synthesizer for output. The results are a little loose but definitely recognizable.
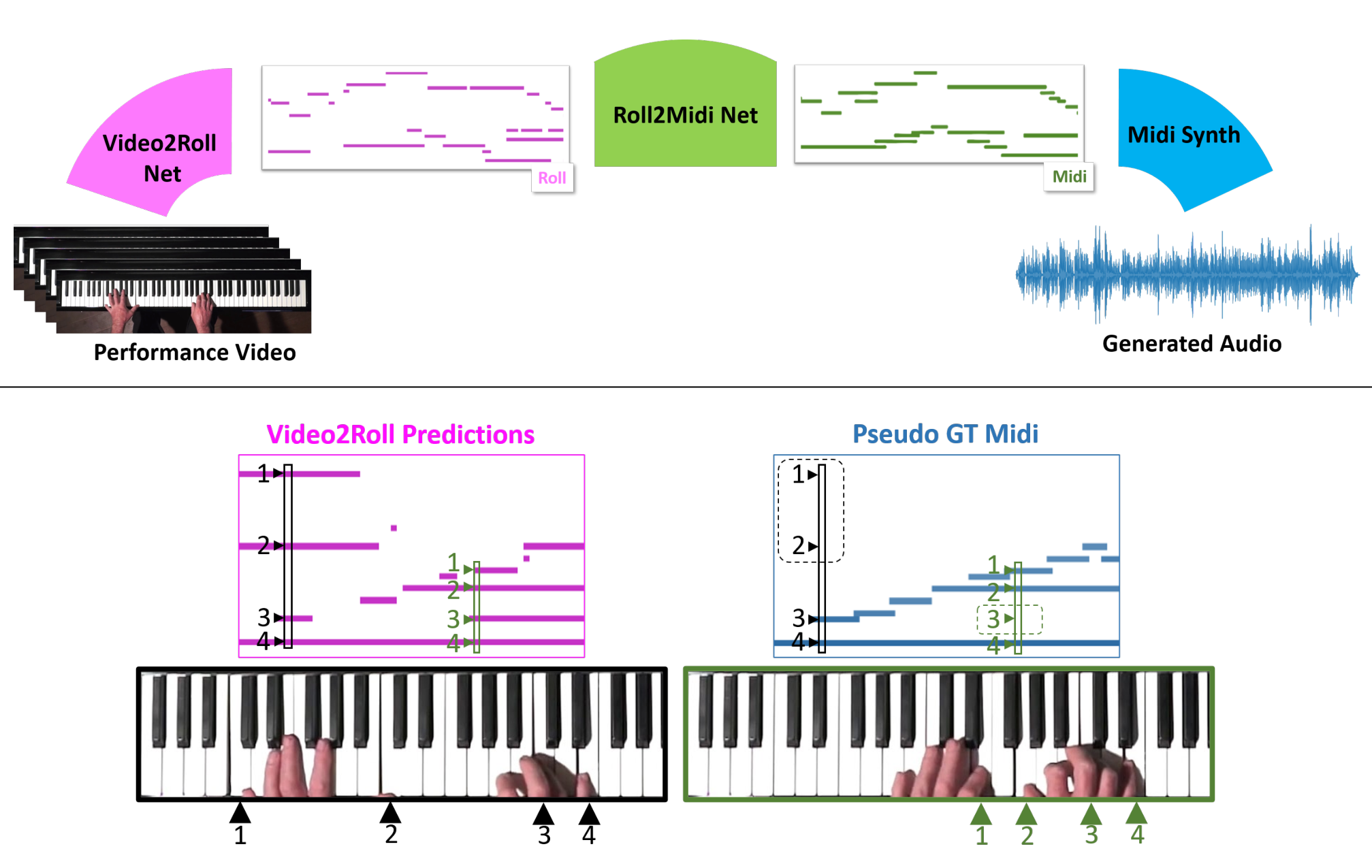
“To create music that sounds like it could be played in a musical performance was previously believed to be impossible,” said Shlizerman. “An algorithm needs to figure out the cues, or ‘features,’ in the video frames that are related to generating music, and it needs to ‘imagine’ the sound that’s happening in between the video frames. It requires a system that is both precise and imaginative. The fact that we achieved music that sounded pretty good was a surprise.”
Another from the field of arts and letters is this extremely fascinating research into computational unfolding of ancient letters too delicate to handle. The MIT team was looking at “locked” letters from the 17th century that are so intricately folded and sealed that to remove the letter and flatten it might permanently damage them. Their approach was to X-ray the letters and set a new, advanced algorithm to work deciphering the resulting imagery.
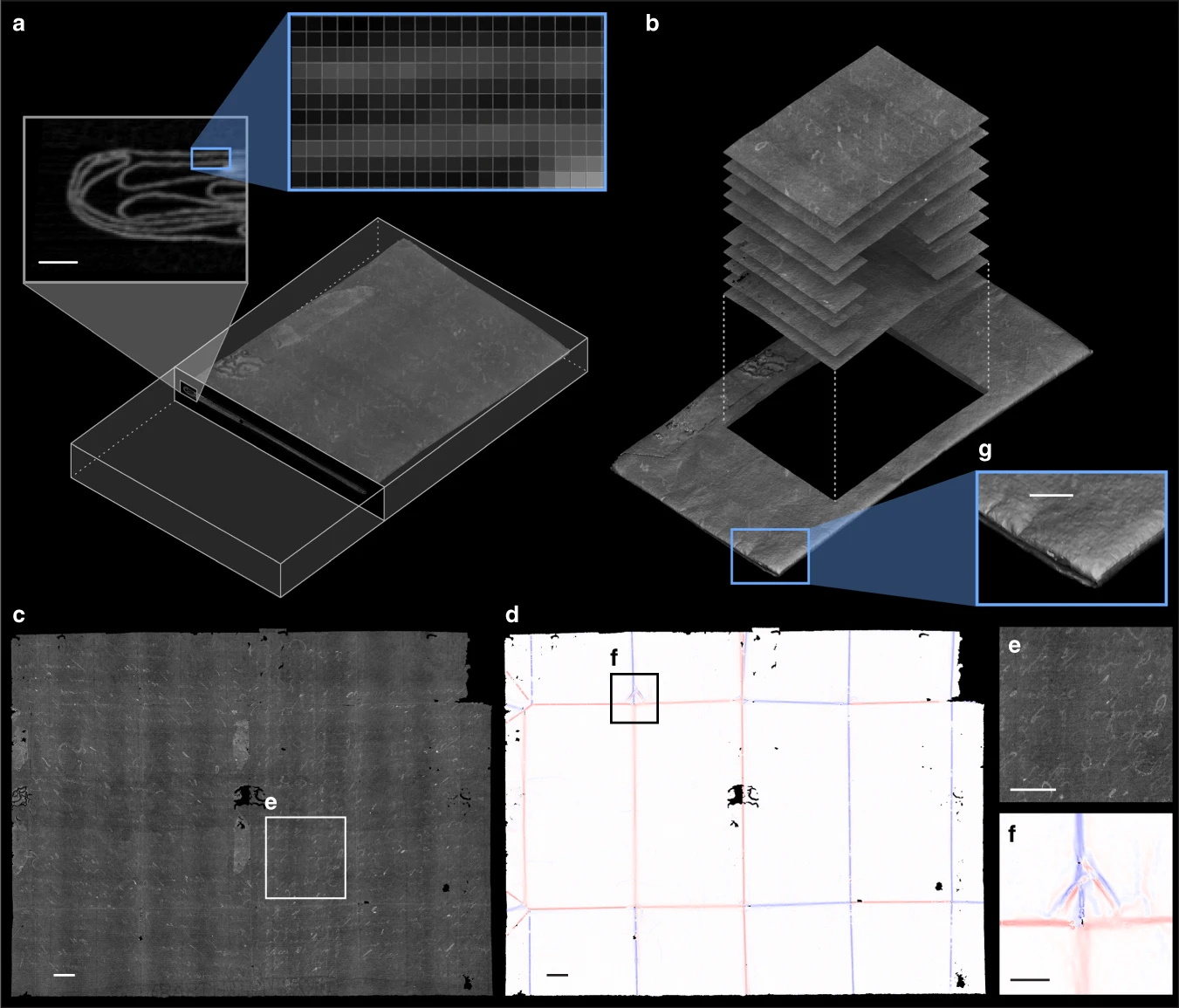
“The algorithm ends up doing an impressive job at separating the layers of paper, despite their extreme thinness and tiny gaps between them, sometimes less than the resolution of the scan,” MIT’s Erik Demaine said. “We weren’t sure it would be possible.” The work may be applicable to many kinds of documents that are difficult for simple X-ray techniques to unravel. It’s a bit of a stretch to categorize this as “machine learning,” but it was too interesting not to include. Read the full paper at Nature Communications.
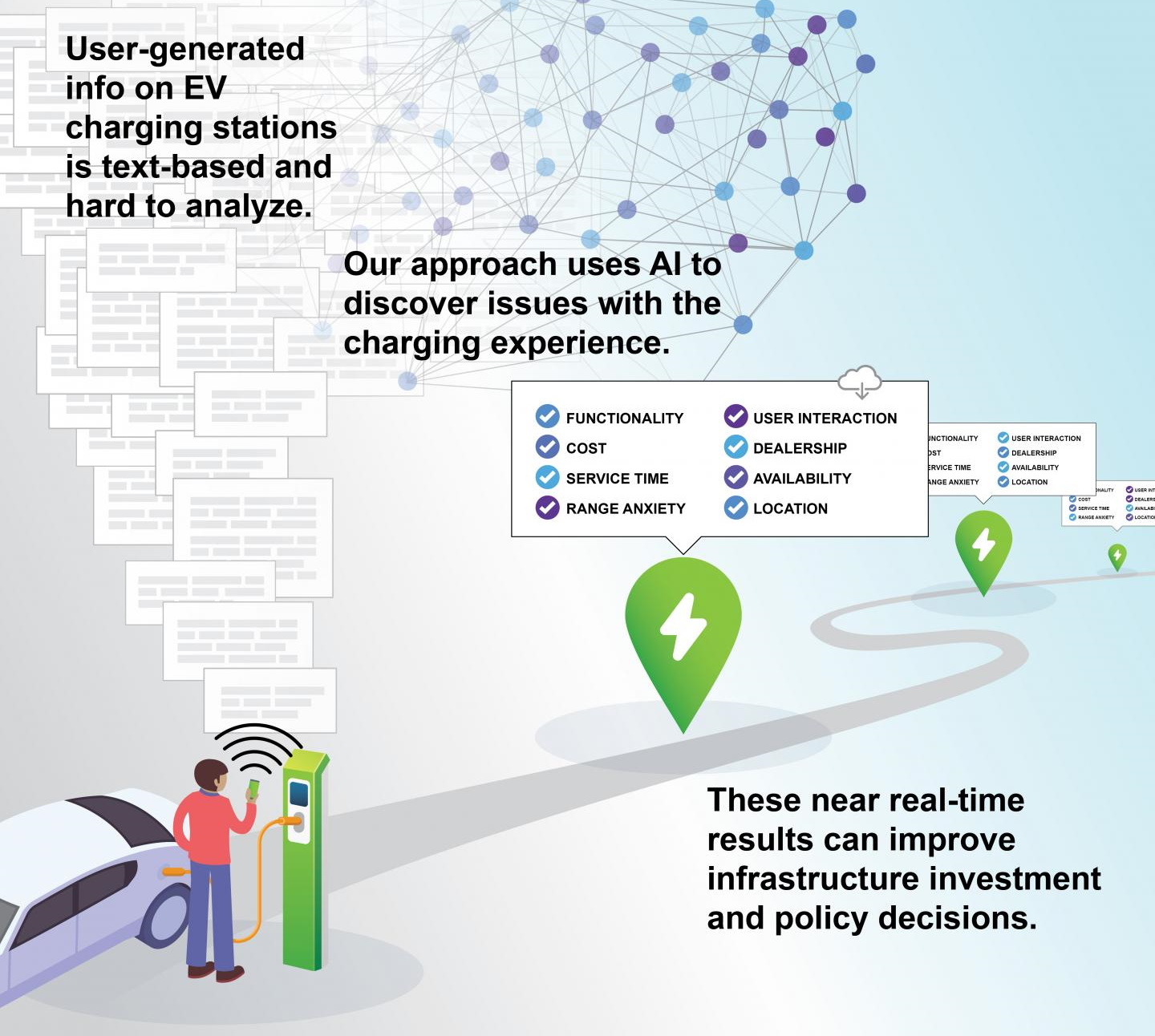
You arrive at a charge point for your electric car and find it to be out of service. You might even leave a bad review online. In fact, thousands of such reviews exist and constitute a potentially very useful map for municipalities looking to expand electric vehicle infrastructure.
Georgia Tech’s Omar Asensio trained a natural language processing model on such reviews and it soon became an expert at parsing them by the thousands and squeezing out insights like where outages were common, comparative cost and other factors.
“Given the massive investment in electric vehicle infrastructure, we’re doing it in a way that is not necessarily attentive to the social equity and distributional issues of access to this enabling infrastructure,” said Asensio. Where better to study those issues than in unsolicited feedback from the people most affected?
Sudden interruptions to service, power or other necessaries can also lead to drones falling out of the air. The more built-in safeties we have in such circumstances, the better — and they can’t rely on anything like control signals or GPS. University of Zurich researchers have shown that a damaged drone with nothing more than a camera and working CPU can retain a pretty good amount of control.
A busted rotor from a collision or mechanical problem can cause a quadcopter to spin wildly and crash. But the Swiss team, led by Sihao Sun, showed that an onboard camera can perform very quick analysis of its surroundings as it spins, estimating its position based on the surroundings zooming by its view.
IEEE Spectrum has more information and an interview with Sun if you want to learn more (and why wouldn’t you?).
The ability to analyze imagery fast is a common asset in today’s AI systems. This has come into play in the medical imaging industry as well, where examinations and instruments can produce more images than a single doctor or even several specialists can be expected to scrutinize closely in a short time frame.
Echocardiograms, or ultrasound images of the heart, are no exception. A single session can yield thousands of images, any one of which might provide the clear image needed by a doctor to form a good idea of the heart’s condition. A team at Geisinger Research showed that AI can help sort through these images and aid doctors in the process of diagnosis and prognosis. The paper published in Nature Biomedical Engineering showed that doctors assisted by the system were 13% more accurate in predicting mortality.
The enormous (nearly 50 million images total) dataset on which it was trained will likely lead to more advances — the discovery here is of the possibility of using an unstructured imagery database like this one to produce decision-aiding AI, not the limits of those possibilities.
The problem of dealing with large amounts of data is mitigated somewhat when that data can be checked by humans. For instance, an image recognition algorithm that sorts pictures of cats from those of dogs can easily have its results audited by a human because we all know what dogs and cats look like.
But what if the neural network is looking at something humans don’t intuitively understand — like DNA sequences? It’s hard to say whether a system works well if the people making it aren’t confident about their ability to monitor it.
Peter Koo and Matt Ploenzke at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory looked into ways of making machine learning systems made to analyze genomic sequences a bit more transparent to humans. It involves strong training of one layer of the convolutional neural network with known, familiar patterns so that the network uses those as points of reference in its analysis later. These improvements to interpretability seem to be independent of overall model effectiveness, so Koo speculates that if designed right, there should be no real trade-off.
Back to the arts and letters theme. Interpretability is as important when AIs make mistakes as when they get good results. A strange case appeared recently as CMU researchers showed that YouTube and other major implementers of natural language processing may be mistakenly flagging some chatter as inappropriate due to a misunderstanding of chess terminology.

It suddenly seems obvious when you consider that chess is often discussed in terms of white versus black, and in certain constructions — “white made a savage attack on black and drove him back” or the like — a computer with no real understanding of these terms might think something is awry.
It’s important not just so people can discuss chess freely, but because companies like YouTube need to be able to understand, and explain to their users, why increasingly AI-powered moderation processes make the decisions they do.
Finally, an experiment along those lines showcasing the limits of AI understanding. The famous example of an image analysis system mistaking grass for sheep is a valuable lesson, but another way of looking at what an AI pays attention to is to simply progressively delete more and more of an image and see if it can still recognize it.

This is more of an art project than science (indeed it is by Korean artists Shinseungback Kimyonghun), but the implications are very interesting. When you’ve taken away everything that an AI recognizes about a scene, what is left? In some cases, the landscape is, in a way, almost as clear to the human eye as it was to start with. It’s a reminder of how different our mode of perception is from the machine learning systems we’ve created to ape it.
Create a handbook and integrate AI to onboard remote employees
Early Stage is the premier ‘how-to’ event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear first-hand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company-building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in – there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.






























Comment