Instacart is not done making news.
Earlier this week, the well-known grocery delivery unicorn announced a software suite as part of a self-described third act. Today, Bloomberg reported that Instacart reduced its valuation from around $39 billion to $24 billion, representing a roughly 38.5% reduction in the company’s worth.
Commentary indicates that the company’s new “valuation” was set by a 409a price change, not a decrease in the value of preferred shares sold in its last round. The nuance at play here is that 409a valuations are set by third parties – Carta does this work for customers, as an example – and not startups or their venture investors, resulting in a more objective price by some measures. That said, what we presume to be a newly set 409a valuation for Instacart does matter.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on TechCrunch+ or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
The valuation change fits into the larger trend of the value of high-growth technology companies flagging in recent months. From late-2021 highs, the public markets have slashed the value of tech companies large and small, SaaS and otherwise. Instacart, which has a number of public comps thanks to IPOs from DoorDash and Uber, lives in a world where it can directly compare its worth to floating concerns.
The Exchange dug into the Instacart valuation change and has a few notes on the company’s current trajectory. The changing public market issue is only one theme at play in Instacart’s smaller valuation. The other is human talent. Let’s explore.
$24 billion is the new $39 billion
Instacart said that it set a number of records in 2021, including order volume, gross transaction volume, revenue and gross profit. The company also has more than $1 billion in cash and equivalents in the bank, so it’s far from low on capital.
Bloomberg also reported that the company saw $1.8 billion in 2021 revenues, up from prior reporting that the company was on target for $1.65 billion in top-line last year. At the higher figure, and Instacart’s new valuation, the company sports a 13.3x trailing revenue multiple. (Note that this is a more conservative metric than an ARR multiple that we calculate for pure software companies.) At the company’s prior $39 billion price tag, its 2021 revenues would have given it a far greater 21.7x multiple.
Instacart is not the only grocery-delivery company that has seen its revenue multiple decline in recent months.
DoorDash, which delivers both prepared foods and grocery items, has also seen its price-sales ratio fall from 2021 highs (via YCharts):
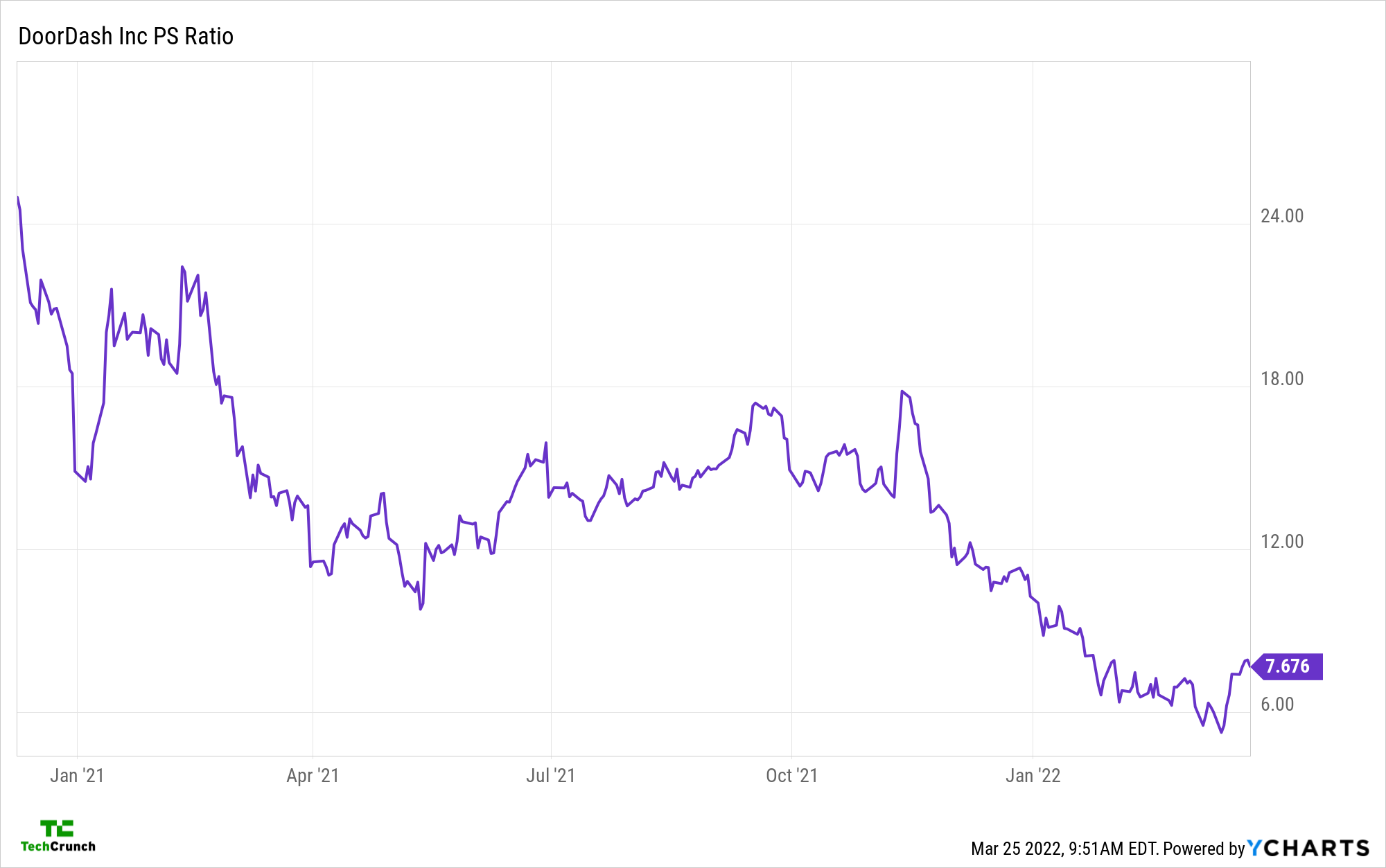
Uber, which is working on scaling its grocery delivery business as part of a larger food delivery push that complements its ride-hailing efforts, sports an even smaller price-sales ratio than DoorDash. You can imagine the pressure that Instacart felt with its more static private market sitting pat while its rivals were re-priced.
The change in price won’t enthuse the company’s most recent investors – no one likes losses, paper or otherwise. But the change is helpful for a more important constituency: employees. Employees of startups get paid partially in stock, a mechanism that depends on the value of the company in question. If the valuation is too high, employees may have their equity grants priced at a level that doesn’t match what the market considers a fair value, leading to upside-down grants and harder hiring at the corporate level.
By cutting its paper valuation, Instacart is effectively able to offer more stock to new employees, and more fairly compensate its existing staff, by our understanding of startup comp practices. Given the wildly competitive talent market that persists into 2022, the move makes sense.
Our question is simple: Will other unicorns follow suit?
Startup impact?
Before wondering if Instacart is setting a new trend, it is worth keeping in mind that it also joins one.
While Instacart’s decision is noteworthy, there have been other examples of companies lowering their valuation before an IPO. Quite a few of these examples are recent and happened around the same time as some bumpy tech listings.
For instance, proptech company Compass downsized its IPO plans in late March 2021 on the same day as Deliveroo’s rough public debut. And if we are talking about pre-IPO repricing, this also happened to neobank Nubank, whose parent company Nu Holdings lowered expectations from its initial filing.
But when we talk about lowering the price at which public shares will be sold, or reducing their number, we are talking about companies that are already in the middle of an IPO. And in a way, finding the right price is also part of the process. This is also what some companies are trying to avoid thanks to direct listings.
Instacart, on the other hand, hasn’t made formal moves toward an IPO yet that we are aware of. The operation isn’t on the calendar, and our feeling is that it won’t be happening for some time. Considering how slow the IPO market has been of late, and the current public market climate, we are tempted to say that it is still a few quarters out.
If Instacart’s IPO isn’t imminent, its most immediate concern might not be how it would fare when going public. Instead, it’s talent and how an overvaluation might affect it that seems to weigh the most.
Many late-stage startups are in the same position as Instacart: They have publicly listed competitors whose market multiples are much higher than theirs. And they know that candidates are increasingly sophisticated and empowered, meaning that they won’t be interested in worthless or underwater options.
The same causes lead to the same conclusions, which make us think that others will follow Instacart’s path and commit to a lower valuation.
The details of Instacart’s decisions also matter here: You can’t only focus on hiring to the detriment of existing employees. Because of this, Instacart isn’t only talking about future employees’ stock, but also noting that it is trying to make adjustments for existing employees. No doubt that HR people across late-stage companies everywhere will be taking notes.































Comment