Botnets have increasingly become the vehicle of choice to deliver crypto-mining malware. By infecting various corporate assets such as servers and IoT devices, cyber-criminals can use the collective processing power of hundreds – or thousands – of machines to mine cryptocurrency and spread to further devices.
This blog explores how an Internet-facing server was breached in a company in Singapore. The threat actors used the device to move laterally and deploy crypto-mining software. Within two days, several devices in the company had begun cryptocurrency mining.
Creating the botnet
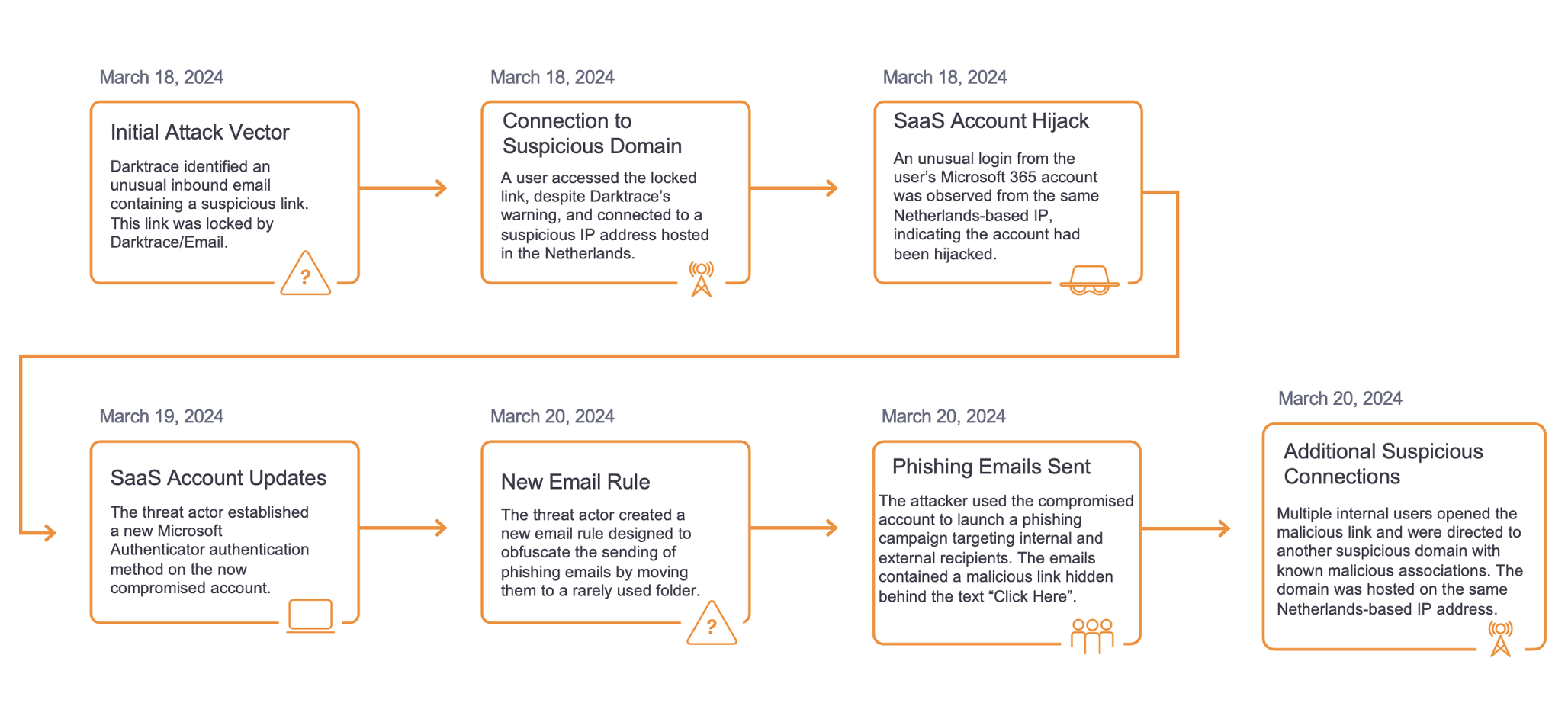
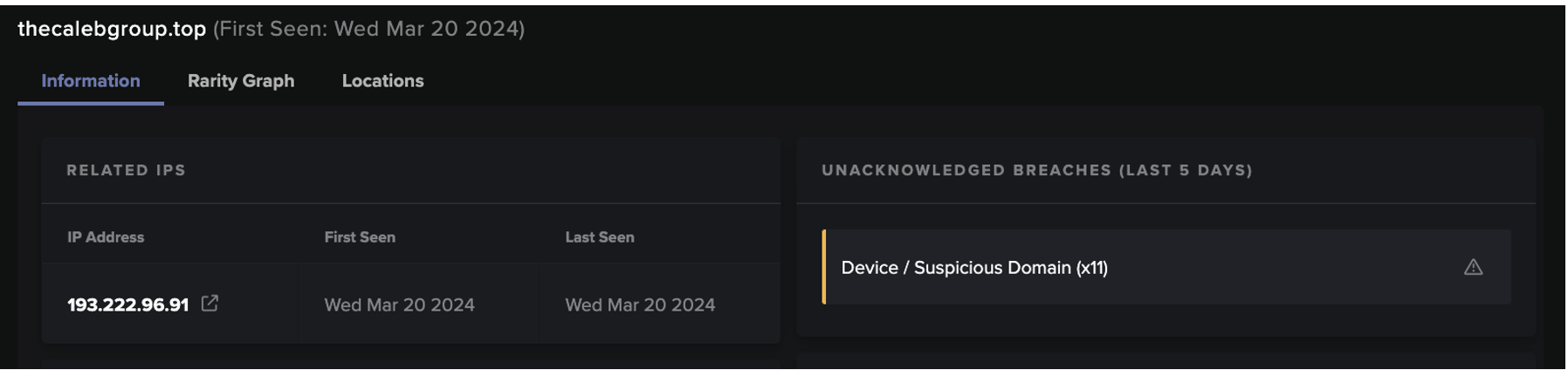
Only a few days after Darktrace had been installed in a Proof of Value (POV) trial, it detected a server in the company downloading a malicious executable from a rare endpoint, 167.71.87[.]85.

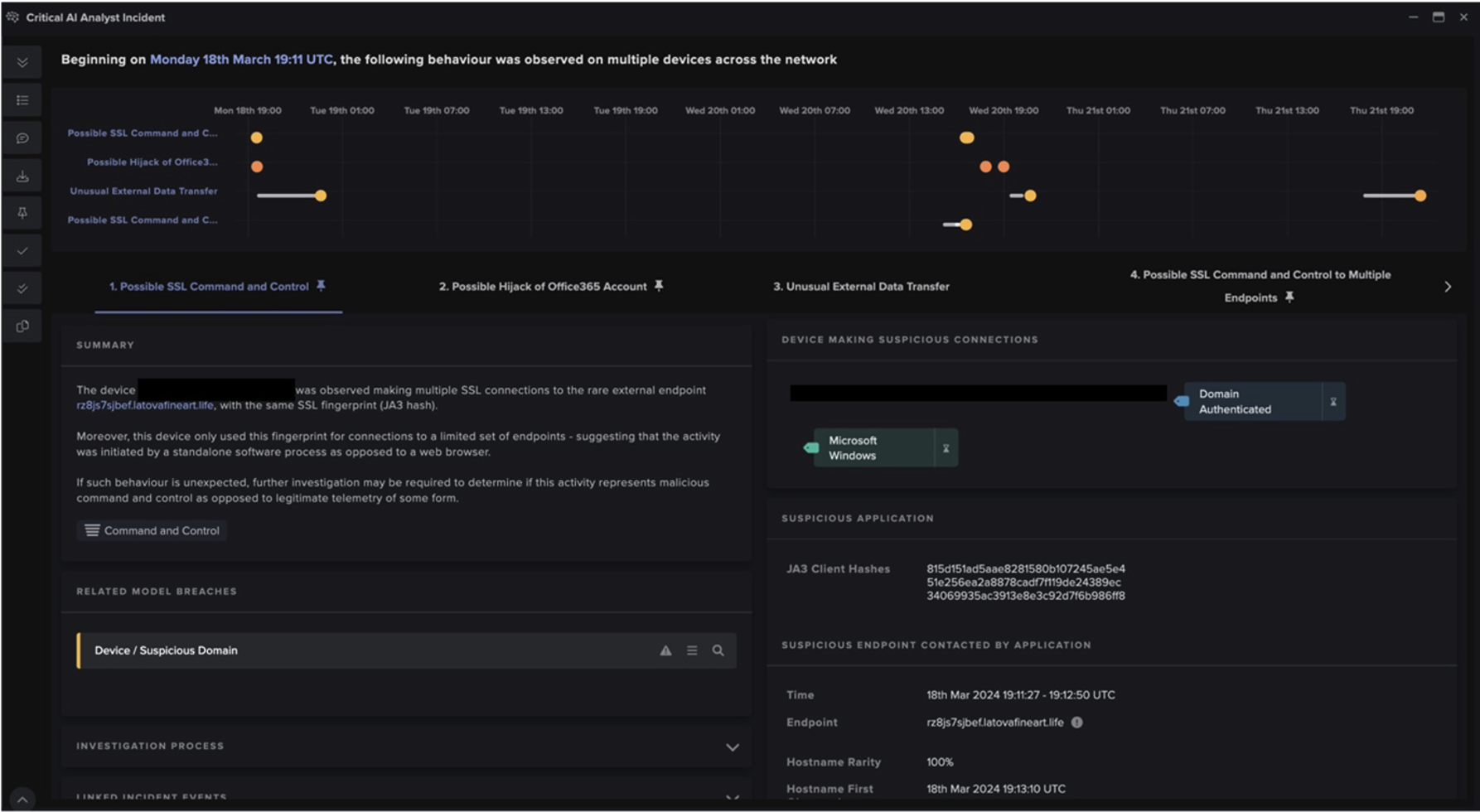
Figure 1: Timeline of the attack.
The server was observed making HTTP connections to a range of rare external endpoints, without a user agent header. The main hostname was t[.]amynx[.]com, a domain on open-source intelligence (OSINT) associated with crypto-mining trojans.
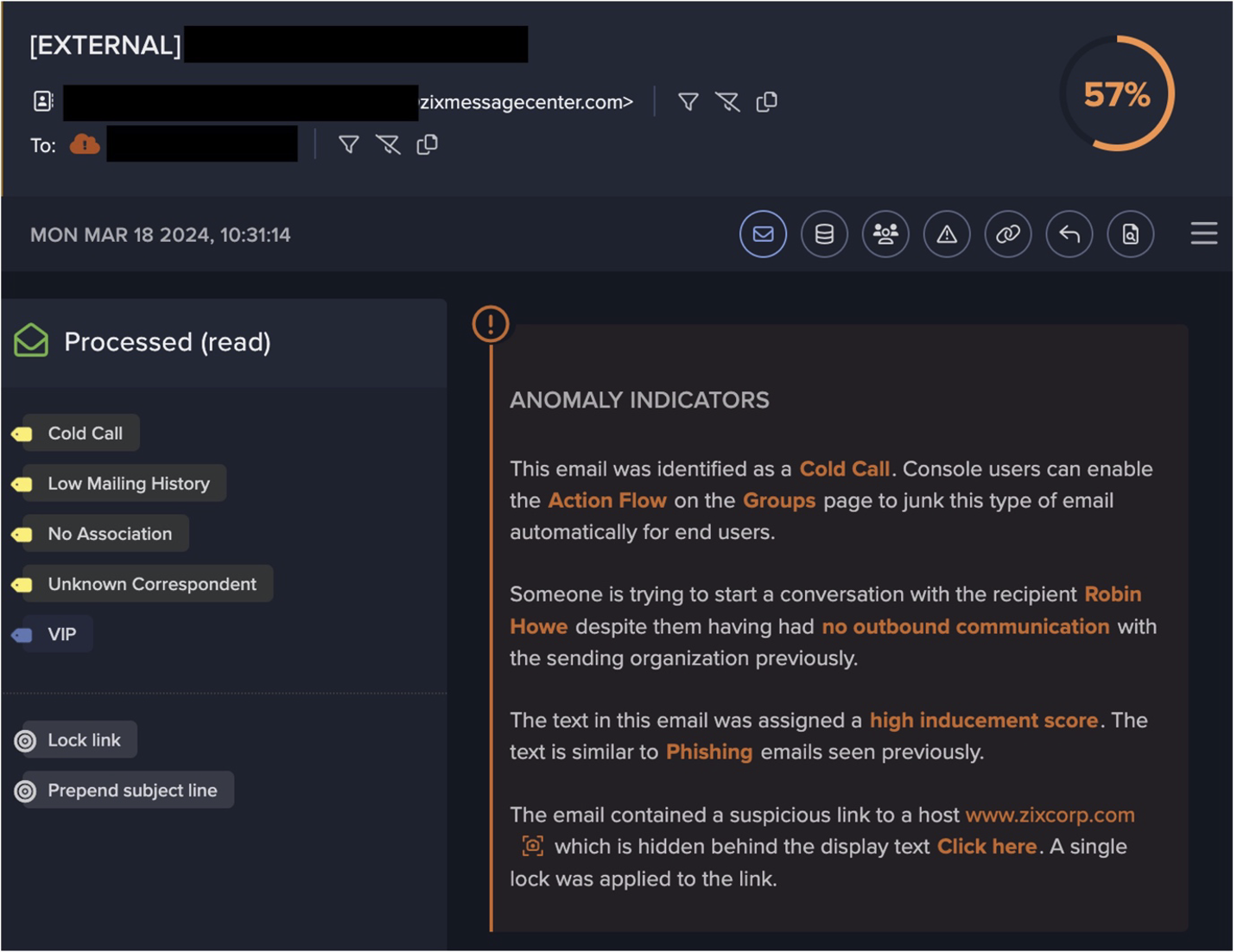
The device initiated repeated external connections to a range of external IPs over the TCP port 445 (SMB). This was followed by an unusually large number of internal connection attempts to a wide range of devices, suggesting scanning activity.
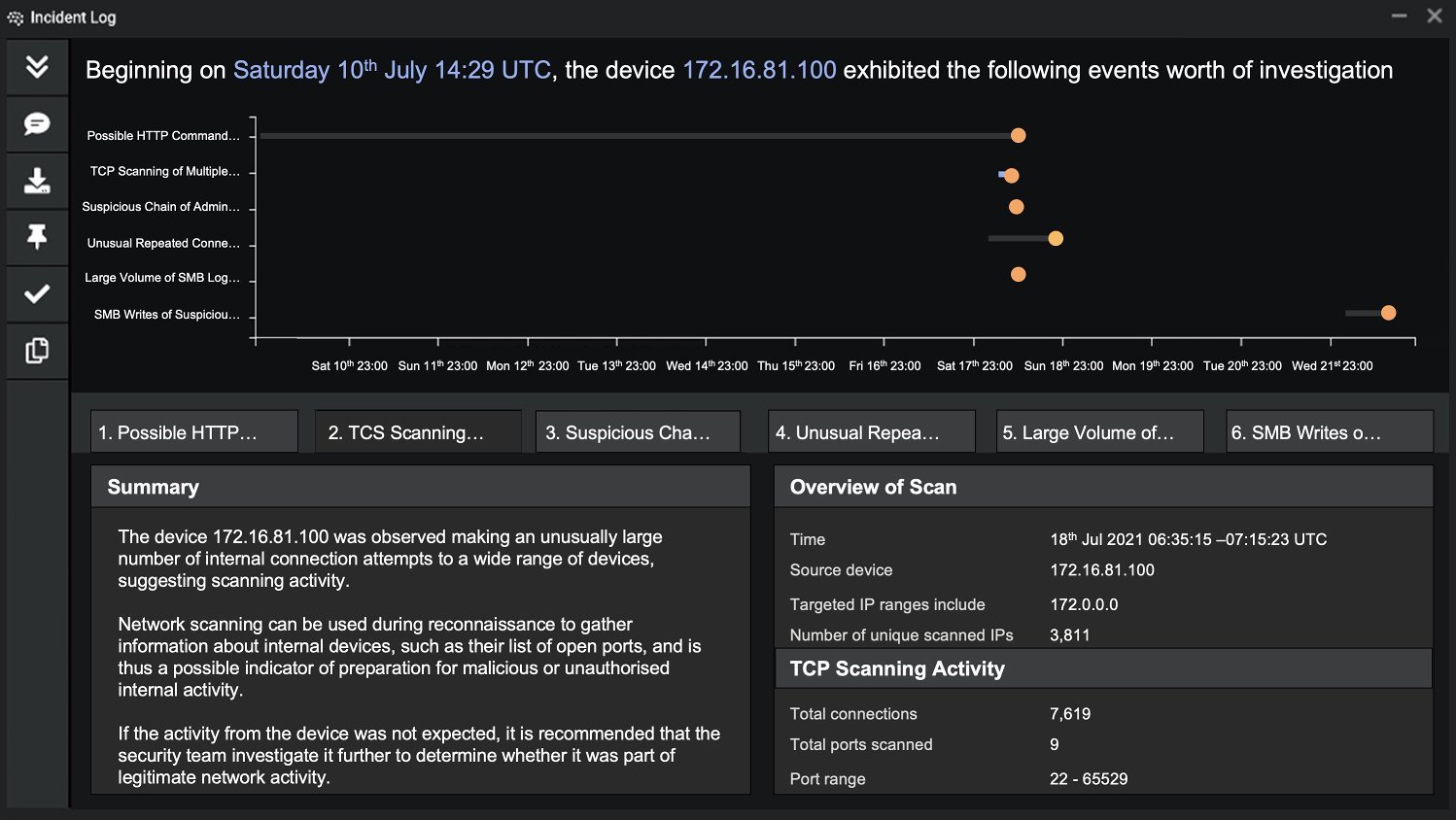
Figure 2: Details for the TCP scanning activity in a similar incident — note the consolidation of six relevant events into one summary.
Growing the botnet
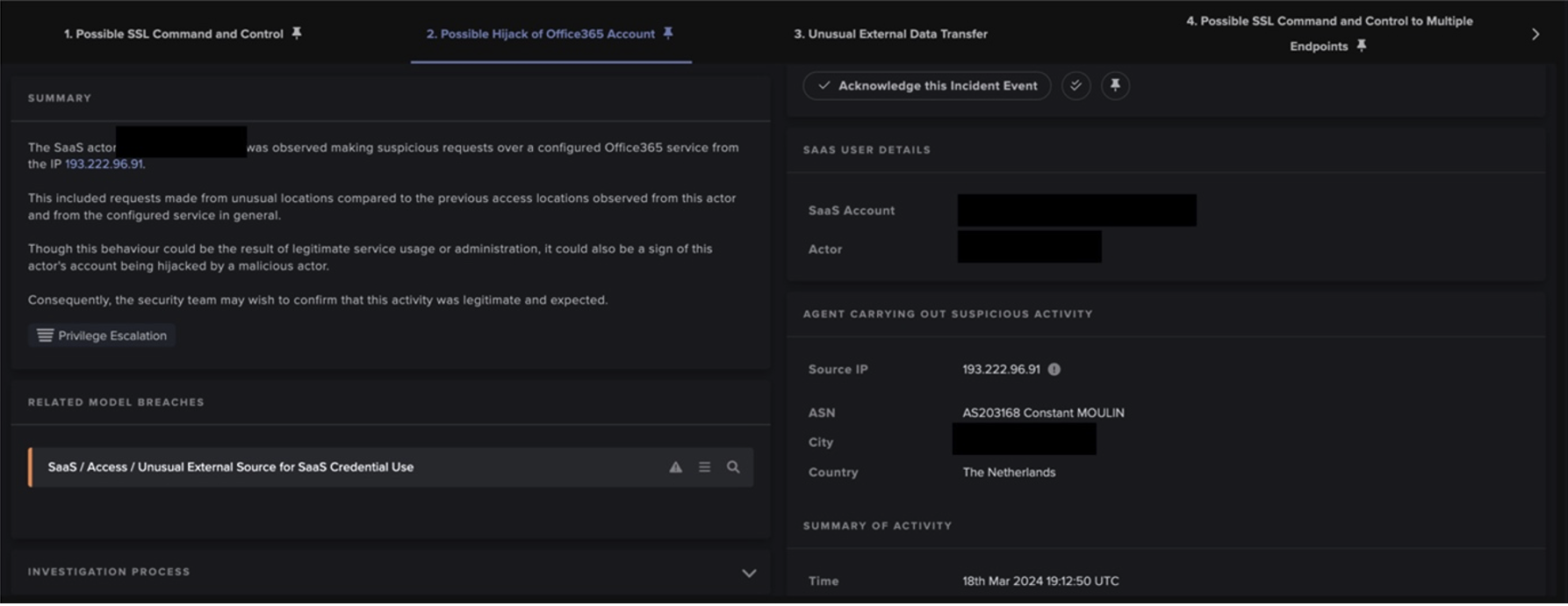
The malware began to move laterally from the initially infected server, predominantly by establishing chains of unsual RDP connections. Subsequently, the server started making external SMB and RPC connections to rare endpoints on the Internet, in an attempt to find further vulnerable hosts.
Other lateral movement activities included the repeated failing attempts to access multiple internal devices over the SMB file-sharing protocol, with a range of different usernames. This implies bruteforce network access, as the threat actor attempted to guess correct account details through trial and error.
Existing tools such as RDP and Windows Service Control reveal that the attacker was employing ‘Living off the Land’ techniques. This makes a system administrator’s job inherently harder, as they must distinguish the malicious use of built-in tools versus their legitimate application.
Crypto-mining begins
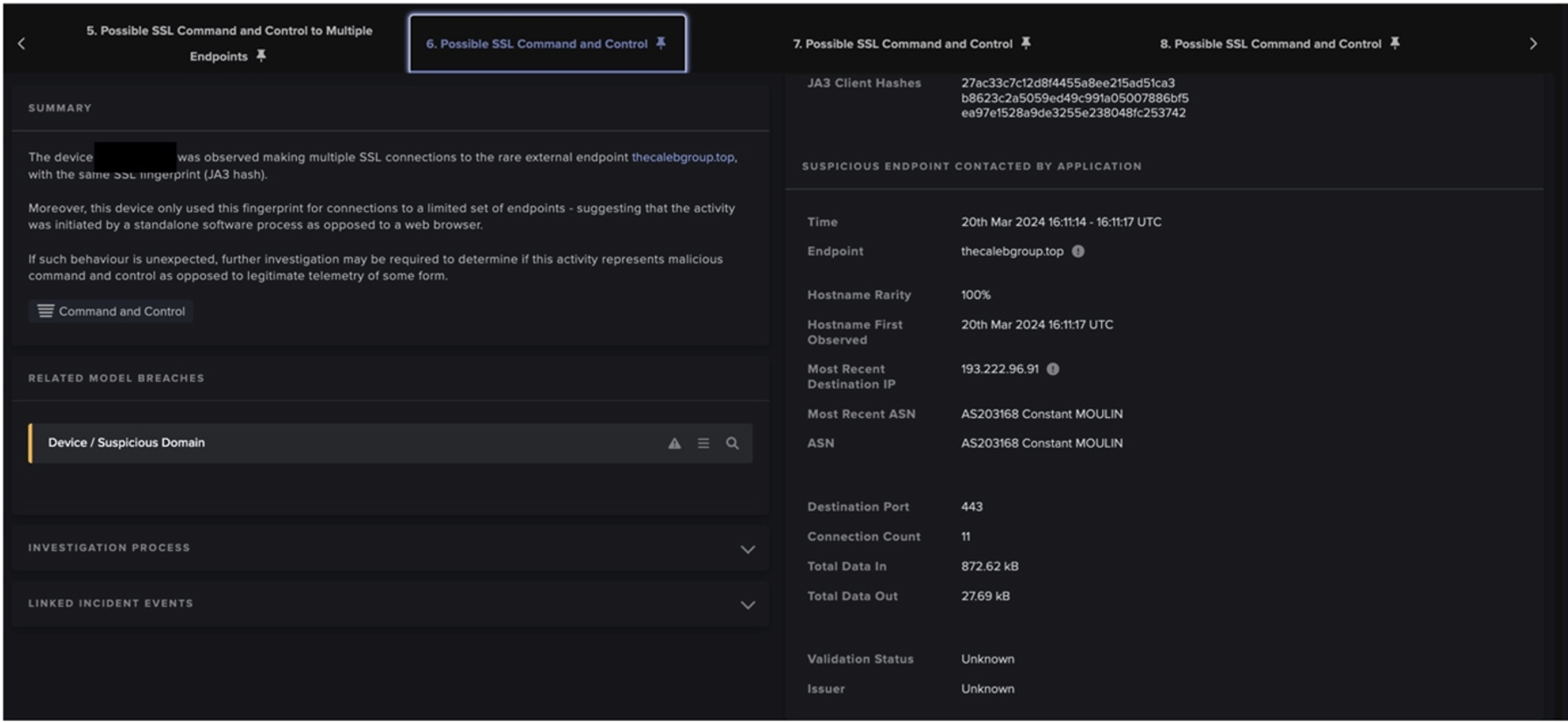
Finally, the compromised server completed the lateral movement by transferring suspicious executable files over SMB to multiple internal devices, with names that appear randomly generated (e.g. gMtWAvEc.exe, daSsZhPf.exe) to deploy crypto-mining malware using the Minergate protocol.
Minergate is a public mining pool utilized for several types of cryptocurrency including Bitcoin, Monero, Ethereum, Zcash, and Grin. In recent months, ransomware actors have begun shifting away from Bitcoin towards Monero and other more anonymous cryptocurrences – but crypto-miners have been using altcoins for years.

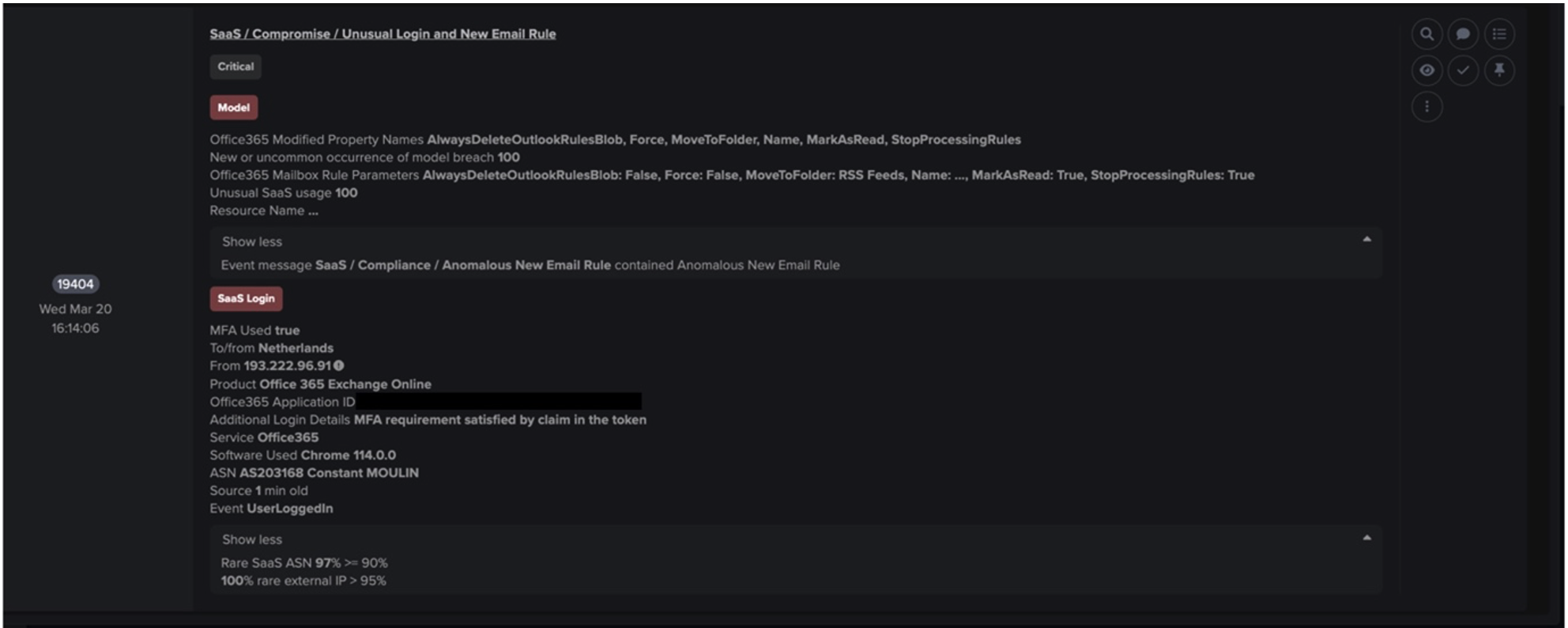
Figure 3: The graph shows a clear increase in model breaches on a similar device, which easily identifies the time frame for the compromise.
As this was part of a trial, Antigena – Darktrace’s Autonomous Response capability – was not in active mode and so could not take action to stop the initial vector of infection. However, the Antigena model “Antigena / Network / External Threat / Antigena Suspicious File Block” was breached on July 18 at 03:55:45. If active, Antigena would have instantly blocked connections to 167.71.87[.]85 on port 80 for two hours, allowing the security team enough time to remediate the breach.
Crypto-mining malware: All the rage
Crypto-mining attacks are extremely common. Although not as destructive as ransomware, they can have a serious impact on network latency and take a long time to detect and clean up. While the infection remains unnoticed, it provides a backdoor into the victim organization – and could switch from conducting crypto-mining to delivering ransomware at any moment. In this case, it is clear the attacker aimed to create maximum disruption by transferring malicious software with targets such as internal servers and domain controllers.
Darktrace detected every step of the attack without relying on known indicators of threat. Cyber AI Analyst automated the complete investigation process, saving the security team crucial time during the live incident.
Especially with the recent crackdowns on Bitcoin farms in China, underground botnets and cloud-based crypto-mining are likely to become more prominent. As we see more of these intrusions in the near future, AI-powered detection, investigation, and response, will prove critical in defending organizations of all sizes, at all times.
Learn more about crypto-mining malware
IoCs:
IoCComment167.71.87[.]85Malware Download — SHA1: 6a4c477ba19a7bb888540d02acdd9be0d5d3fd02VirusTotalt[.]amynx[.]comHTTP Command and Control – recently created domain with suspicious indicators on OSINT sites (associated with cryptomining trojans)AlienVaultVirusTotallplp[.]ackng[.]comCrypto Currency Mining Activity (Minergate)VirusTotalgMtWAvEc.exedaSsZhPf.exeyAElKPQi.exeExamples of malicious executables
Darktrace model breaches:
- Antigena / Network / Insider Threat / Antigena Network Scan Block
- Device / Suspicious Network Scan Activity
- Device / Large Number of Model Breaches
- Device / Multiple Lateral Movement Model Breaches (x2)
- Unusual Activity / Successful Admin Bruteforce Activity
- Anomalous Connection / SMB Enumeration
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Controlled and Model Breach (x2)
- Antigena / Network / External Threat / Antigena Suspicious File Block
- Compromise / Beacon to Young Endpoint (x4)
- Device / Possible RPC Lateral Movement
- Antigena / Network / Insider Threat / Antigena SMB Enumeration Block
- Compromise / Beaconing Activity To External Rare (x5)
- Anomalous Server Activity / Denial of Service Activity
- Antigena / Network / External Threat / Antigena Suspicious Activity Block (x4)
- Device / Large Number of Connections to New Endpoints
- Device / Network Scan - Low Anomaly Score
- Anomalous Connection / New or Uncommon Service Control (x3)
- Device / New User Agent To Internal Server
- Device / Anomalous RDP Followed By Multiple Model Breaches (x3)
- Device / Anomalous SMB Followed By Multiple Model Breaches (x3)
- Device / SMB Session Bruteforce (x2)
- Device / Increased External Connectivity
- Device / Network Scan
- Compromise / High Volume of Connections with Beacon Score (x5)
- Unusual Activity / Unusual External Activity (x3)
- Anomalous Connection / Unusual Admin SMB Session
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Significant Anomaly from Client Block
- Compliance / SMB Drive Write (x3)
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Breaches Over Time Block (x14)
- Compliance / Internet Facing RDP Server
- Anomalous Connection / Multiple Failed Connections to Rare Endpoint (x5)
- Compliance / Outbound RDP (x3)
- Anomalous Server Activity / Rare External from Server (x5)
- Compromise / Slow Beaconing Activity To External Rare (x8)
- Anomalous Server Activity / Outgoing from Server (x2)
- Device / New User Agent
- Anomalous Connection / New Failed External Windows Connection (x5)
- Compliance / External Windows Communications
- Device / New Failed External Connections (x7)
- Compliance / Crypto Currency Mining Activity (x9)
- Compliance / Incoming Remote Desktop (x9)