Generative AI is disrupting industries — with understandable controversy.
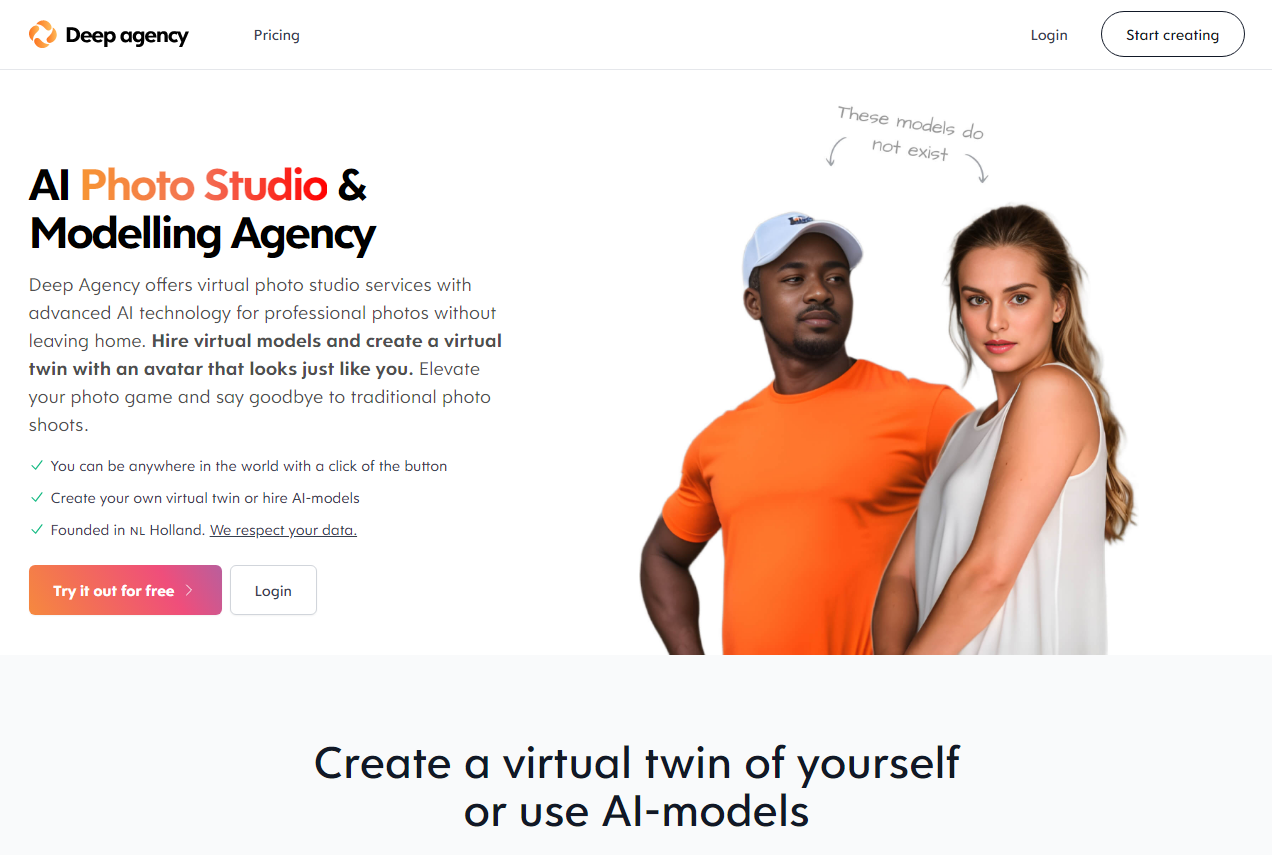
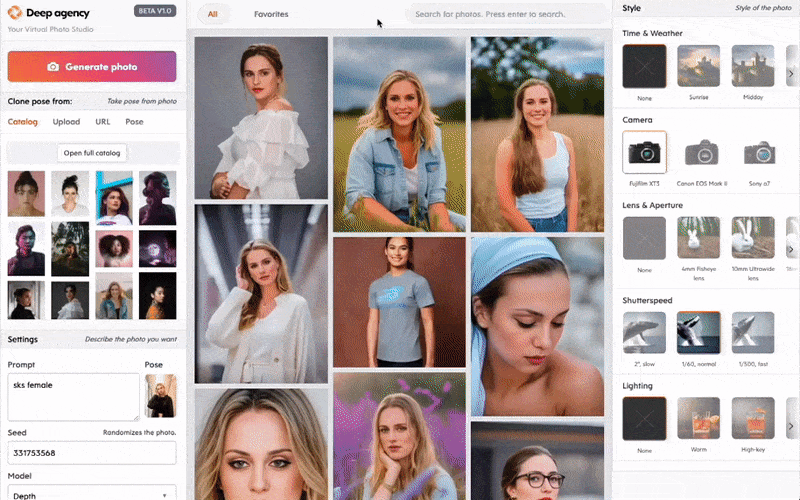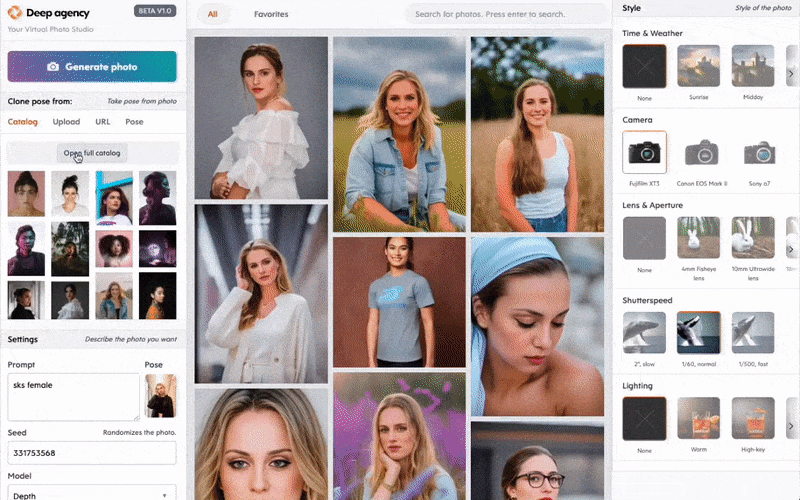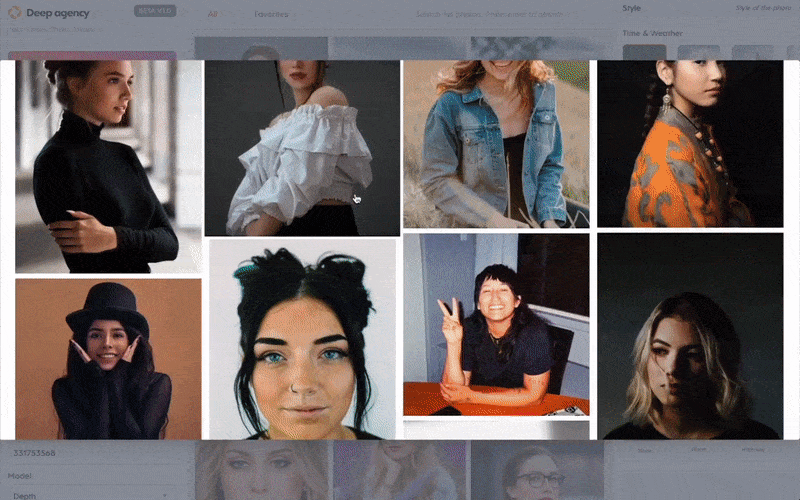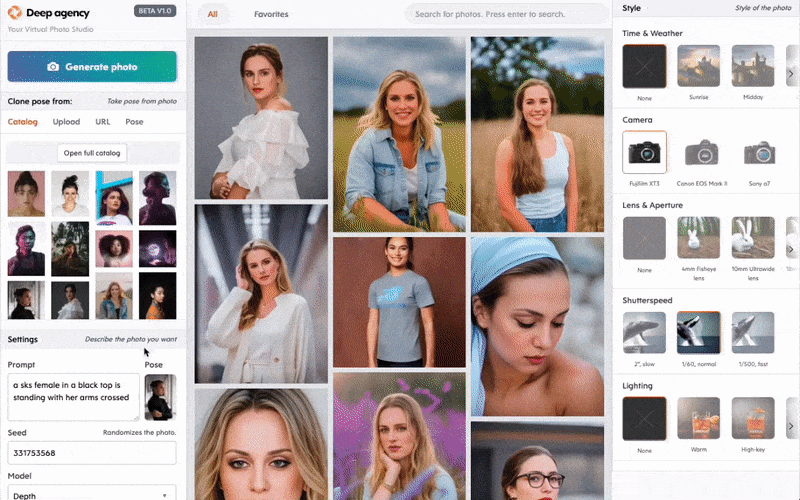
Earlier this month, Danny Postma, the founder of Headlime, an AI-powered marketing copy startup that was recently acquired by Jasper, announced Deep Agency, a platform he describes as an “AI photo studio and modeling agency.” Using art-generating AI, Deep Agency creates and offers “virtual models” for hire starting at $29 per month (for a limited time), letting customers place the models against digital backdrops to realize their photoshoots.
“What is Deep Agency? It’s a photo studio, with a few big differences,” Postma explained in a series of tweets. “No camera. No real people. No physical location … What’s this good for? Tons of things, like automating content for social media influencers, models for marketeers’ ads and ecommerce product photography.”
Deep Agency is very much in the proof-of-concept phase, which is to say… a tad borked. There’s a lot of artifacting in the models’ faces, and the platform places guardrails — intentional or not — around which physiques can be generated. At the same time, Deep Agency’s model creation is strangely hard to control; try generating a female model dressed in a particular outfit, like a police officer’s, and Deep Agency simply can’t do it.
Nevertheless, the reaction to the launch was swift — and mixed.
Some Twitter users applauded the tech, expressing an interest in using it for modeling clothing and apparel brands. Others accused Postma of pursing a “deeply unethical” business model, scraping other peoples’ photography and likenesses and selling it for profit.
The divide reflects the broader debate over generative AI, which continues to attract astounding levels of funding while raising a host of moral, ethical and legal issues. According to PitchBook, investments in generative AI will reach $42.6 billion in 2023 and skyrocket to $98.1 billion by 2026. But companies including OpenAI, Midjourney and Stability AI are currently embroiled in lawsuits over their generative AI technologies, which some accuse of replicating the works of artists without fairly compensating them.
Deep Agency seems to have especially touched a nerve because of the application — and implications — of its product.
Postma, who didn’t respond to a request for comment, isn’t shy about the fact that the platform could compete with — and perhaps harm the livelihoods of — real-world models and photographers. While some platforms like Shutterstock have created funds to share revenue from AI-generated art with artists, Deep Agency has taken no such step — and hasn’t signaled that it intends to.
Coincidentally, only weeks after Deep Agency’s debut, Levi’s announced that it would partner with design studio LaLaLand.ai to create customized AI-generated models to “increase the diversity of models shoppers can see wearing its products.” Levi’s stressed that it planned to use the synthetic models alongside human models and that the move wouldn’t impact its hiring plans. But it raised questions as to why the brand didn’t recruit more models with the diverse characteristics it’s seeking, given the difficulty these models have had finding opportunities in the fashion industry historically. (According to one survey, as of 2016, 78% of models in fashion adverts were white.)
In an email interview with TechCrunch, Os Keyes, a PhD candidate at the University of Washington who studies ethical AI, made the observation that modeling and photography — and the arts in general — are areas particularly vulnerable to generative AI because photographers and artists lack structural power. They’re largely low-paid, independent contractors to large companies who look to cost-cut, Keyes notes. Models, for instance, are often on the hook for high agency commission fees (~20%) as well as business expenses, which can include plane tickets, group housing and the promotional materials required to land jobs with clients.
“Postma’s app is — if it works — in fact designed to further kick the chair out from under already-precarious creative workers, and send the money to Postma, instead,” Keyes said. “That’s not really a thing to applaud, but it’s also not tremendously surprising … The fact of the matter is that socioeconomically, tools like this are designed to further core out and concentrate profit.”
Other critics take issue with the underlying technology. State-of-the-art image-generating systems like the type Deep Agency uses are what’s known as “diffusion models,” which learn to create images from text prompts (e.g. “a sketch of a bird perched on a windowsill”) as they work their way through web-scraped training data. At issue in artists’ minds is diffusion models’ tendency to essentially copy and paste images — including copyrighted content — from the data that was used to train them.
Companies commercializing diffusion models have long claimed that “fair use” protects them in the event that their systems were trained on licensed content. (Enshrined in U.S. law, fair use doctrine permits limited use of copyrighted material without first having to obtain permission from the rightsholder.) But artists allege that the models infringe on their rights, in part because the training data was sourced without their authorization or consent.
“The legality of a startup like this isn’t entirely clear, but what is clear is that it’s aiming to put a lot of people out of work,” Mike Cook, an AI ethicist and member of the Knives and Paintbrushes open research group, told TechCrunch in an email interview. “It’s hard to talk about the ethics of tools like this without engaging with deeper issues relating to economics, capitalism and business.”
There’s no mechanism for artists who suspect their art was used to train Deep Agency’s model to remove that art from the training dataset. That’s one worse than platforms like DeviantArt and Stability AI, which provide ways for artists to opt out of contributing art to train art-generating AI.
Deep Agency also hasn’t said whether it’ll consider establishing a revenue share for artists and others whose work helped to create the platform’s model. Other vendors, such as Shutterstock, are experimenting with this, drawing on a combined pool to reimburse creators whose work is used to train AI art models.
Cook points out another issue: data privacy.
Deep Agency provides a way for customers to create a “digital twin” model by uploading around 20 images of a person in various poses. But uploading photos to Deep Agency also adds them to the training data for the platform’s higher-level models unless users explicitly delete them afterward, as outlined in the terms of service agreement.
Deep Agency’s privacy policy doesn’t say exactly how the platform handles user-uploaded photos, in fact, or even where it stores them. And there’s seemingly no way to prevent rogue actors from creating a virtual twin of someone without their permission — a legitimate fear in light of the nonconsensual deepfake nudes models like Stable Diffusion have been used to create.

“Their terms of use actually state that ‘You understand and acknowledge that similar or identical generations may be created by other people using their own prompts.’ This is quite amusing to me because the premise of the product is that everyone can have bespoke AI models that are unique every time,” Cook said. “In reality, they acknowledge the possibility that you may get exactly the same image as someone else did, and that your photos are fed to others for potential use as well. I can’t imagine a lot of big companies liking the prospect of either of these things.”
Another problem with Deep Agency’s training data is the lack of transparency around the original set, Keyes says. That is to say, it’s not clear which images the model powering Deep Agency was trained on (although the jumbled watermarks in its images give clues) — which leaves open the possibility of algorithmic bias.
A growing body of research has turned up racial, ethnic, gender and other forms of stereotyping in image-generating AI, including in the popular Stable Diffusion model developed with support from Stability AI. Just this month, researchers at AI startup Hugging Face and Leipzig University published a tool demonstrating that models including Stable Diffusion and OpenAI’s DALL-E 2 tend to produce images of people that look white and male, especially when asked to depict people in positions of authority.
According to Vice’s Chloe Xiang, Deep Agency only generates images of women unless you purchase a paid subscription — a problematic bias off the bat. Moreover, Xiang writes, the platform tends to skew toward creating blonde white female models even if you select an image of a woman of a different race or likeness in the pre-generated catalog. Changing a model’s look requires making additional, not-so-obvious adjustments.
“Image-generating AI is fundamentally flawed because it depends on the representativeness of the data the image-generating AI was trained on,” Keyes said. “If it predominantly includes white, Asian and light-skinned Black people, all the synthesis in the world won’t provide representation for darker-skinned people.”
Despite the glaring issues with Deep Agency, Cook doesn’t see it or similar tools disappearing anytime soon. There’s simply too much money in the space, he says — and he’s not wrong. Beyond Deep Agency and LaLaLand.ai, startups like ZMO.ai and Surreal are securing big VC investments for tech that generate virtual fashion models, ethics be damned.
“The tools aren’t really good enough yet, as anyone using the Deep Agency beta can see. But it’s only a matter of time,” Cook said. “Entrepreneurs and investors will keep banging their heads against opportunities like this until they find a way to make one of them work.”































Comment