Jag Lamba
It’s not just a feeling: risk across the geopolitical spectrum has been higher than usual in recent years. For businesses with supply chain operations across the world, these risks are hard to avoid. Issues of resiliency and avoiding sanctions are top of mind when it comes to planning out the coming months and years.
Working with suppliers in or near unstable countries creates significant risk for companies, as business continuity grows ever more uncertain as risk increases. That holds true for a supplier’s own supply chain (what we call “subsuppliers”) as well. For most companies, it’s impossible to identify all the subcontractors and subsuppliers they’re connected with across multiple degrees of separation.
Instead of spending inordinate amounts of resources tracking down every subsupplier, businesses should identify which of their vendors can be labeled “critical” to their business continuity. Then, they should focus on tracking and monitoring those vendors’ own critical suppliers and contractors. That will provide an accurate enough snapshot that can be used to more accurately weigh the geopolitical risk of critical suppliers.
Where wars and international conflicts go, sanctions likely follow. As the rapidly evolving situation in Ukraine has proven, the international sanctions landscape can change practically overnight, with new businesses and individuals regularly being designated as “blocked” entities. A company in the U.S. that continues to do business with someone on that list is at risk of significant fines as well as damage to its reputation.
It’s crucial to check who the owners of businesses are in such situations, as the “ultimate beneficial owners” who are sanctioned might not be flagged if a company simply checks for their suppliers on sanction by the name of the company. In my experience, less than 30% of the firms out there are screening beneficial owners against sanctions lists, despite due diligence being required by OFAC.
A lack of transparency in many supply chains is exacerbating these risks. A Deloitte survey found that less than three-quarters of procurement officers report they have good visibility into their critical-tier suppliers, and just 26% said they were able to predict risks among those suppliers. Only 15% of respondents reported visibility into second- and third-tier suppliers.
Businesses need value-driven policies and systems in place to enforce them across the supply chain. A mission-based rubric can govern policies and rules, specifying what actions to take when risks are detected. Supplier management systems to evaluate suppliers based on this rubric and rate their level of risk should be rolled out.
Flexibility is key here — all risks evolve over time, and visibility of how the risk associated with a supplier has changed should be built into supplier management processes. Crucially, these risk evaluations rely on data from suppliers and key subsuppliers, so incorporating efficient data gathering — especially data is collected directly from the supplier — will go a long way in identifying risky suppliers.
Inflation and the downturn are compounding risk
Just as a war next door can shutter a business, so too can a difficult economic environment. The odds of a global recession are significant, and while many companies are preparing to weather the upcoming storm, the simple fact is that some won’t.
Businesses will shutter, and the companies that rely on them will need to pivot quickly. Resiliency is a worry here, too — businesses must have a plan in place if suppliers go under unless they want to miss out on meeting customer demand while they scramble for a replacement.
A better alternative to planning for a supplier ceasing operations is not working with suppliers who will fold. To some, that might sound like wishful thinking: who can know what will happen in the future? But by properly assessing risk, businesses can spot signs of trouble far ahead, and act proactively to step away from risky businesses before they shut down.
Friend-shoring (moving production to friendlier, less risky counties) and reshoring (moving production back to one’s home country) have ticked up in recent years as a way of avoiding higher risk abroad.
The downside to taking this course of action is higher costs. Stabler, friendlier countries are often more expensive, and inflationary pressures make every change a company makes to their supply chain — even the right ones — costlier. Balancing risk and cost is key.
Courses of action
It can be helpful to visualize how a particular vendor represents organizational risk to a customer. There’s a simple matrix that businesses can use to chart any entity and decide on what to do next:
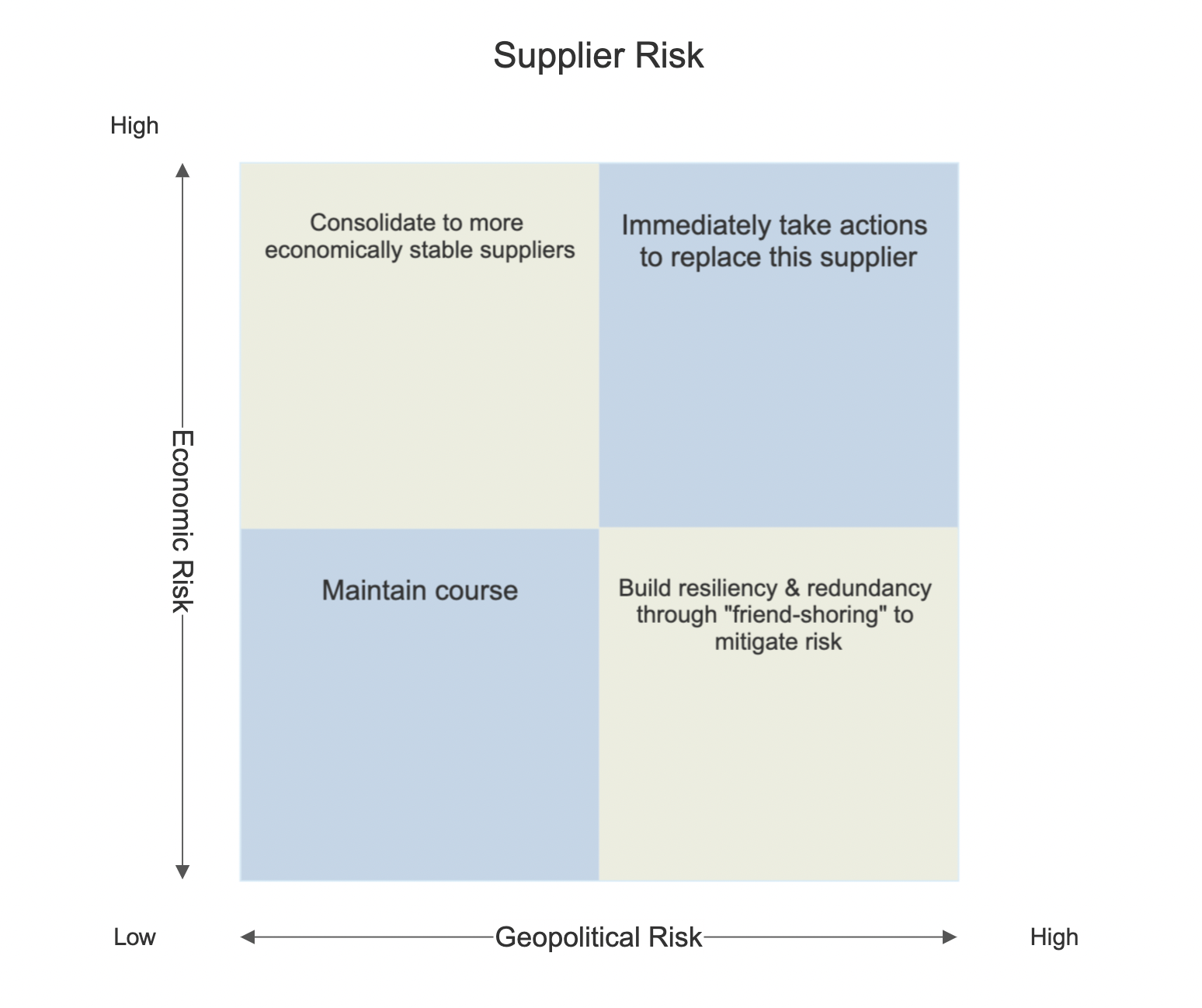
By plotting a supplier based on just two factors — the geopolitical and economic risks described above — businesses can arrive at a prescribed course of action.
Here’s a little more information on what can be considered under each risk heading:
Geopolitical risks
These risks used to be a little harder to catch early, as you had to judge rumors or economic signals carefully to get a sense of what’s coming. Today, the signs of these risks are clearly visible: political instability and regime change, terrorism, international sanctions, piracy, illicit trade, wars, etc. If any of these factors are in play in a supplier’s country, the risks will be higher, and their neighboring countries may also carry some of these risks due to proximity.
Economic risks
These refer to both the risks involving the supplier, and the economic environment it operates in. Is the supplier run by few people, or is it relatively young? Both these factors are traditionally riskier than working with larger or longer-established companies. A company’s performance is also a major factor, as is its position in its industry — not to mention the industry itself.
Based on these two types of risks, suppliers will end up in one of these four quadrants. From there, the recommended course of action is relatively straightforward:
- Low geopolitical risk + Low economic risk: Maintain the course. This is where suppliers should ideally be. Businesses could look to double-down on strategic vendor relationships in this quadrant, and perhaps even vertically integrate with these suppliers by moving business from other riskier parts of the supply chain.
- Low geopolitical risk + High economic risk: Suppliers in this quadrant aren’t great for the long term, as the costs tend to add up. Risk is pricey! The right move here is to consolidate to more economically stable suppliers for longer-term success.
- High geopolitical risk + Low economic risk: Many volatile forces affect suppliers in this quadrant, and it behooves businesses to friend-shore or reshore. It’s best to start small: move 5% of production at first, and then increase that percentage quarterly if the geopolitical risk is still a factor.
- High geopolitical risk + High economic risk: Companies who find themselves placing a supplier in this quadrant should imagine a fire alarm ringing in the background. Replace suppliers who end up here immediately. The risks are high, and will compound on each other. Substantial damage could visit businesses that continue to work with vendors this risky.
Companies should optimize for business continuity: the partners most critical to day-to-day operations should be evaluated first, and if needed, acted upon before you consider others.
ESG: The next frontier of risk
While the economic and geopolitical risks discussed above are common to many businesses, a big risk looms on the horizon, and it should not be ignored.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) requirements are becoming stricter. Addressing sustainability and the environmental impact of a company’s operations will be less an opportunity to differentiate and more of a necessity, similar to earnings reports or following safety guidelines.
This will happen sooner than later, too. The SEC has proposed a mandatory disclosure of climate-change risks, and similar regulations are about to kick in within Europe. Vendors and partners make up two-thirds of the average company’s emissions.
It’s crucial to put in place capabilities to collect, analyze, and report emissions and other sustainability measures immediately. These systems are complex, require the involvement of many parties, and can’t simply be spun up overnight. This includes suppliers, whose emissions are categorized as Scope 3, and are required to be reported in the regulations both coming into effect in Europe and proposed in the United States.
Gaining visibility into the ESG commitments of suppliers already under contract will make it clear which companies are inherently riskier, and which may need to be divested from. Onboarding and assessment tools that include this type of data gathering can ensure that any new suppliers in the future meet a company’s policies for ESG — cutting off that risk before it arrives.
Forging a way forward
By carefully assessing suppliers’ risk levels and taking steps to mitigate the risk, companies can wade more confidently into 2023 and beyond. We have no idea what the next year will hold, except that it’s going to be anything but boring. Businesses that have worked to reduce risks across the globe are likely to be in the best position the next time an event sends shockwaves throughout the world.































Comment