Climate change is affecting farming all over the world, and solutions are seldom simple. But if you could plant crops that resisted the heat, cold or drought instead of moving a thousand miles away, wouldn’t you? Avalo helps plants like these become a reality using AI-powered genome analysis that can reduce the time and money it takes to breed hardier plants for this hot century.
Founded by two friends who thought they’d take a shot at a startup before committing to a life of academia, Avalo has a very direct value proposition, but it takes a bit of science to understand it.
Big seed and agriculture companies put a lot of work into creating better versions of major crops. By making corn or rice ever so slightly more resistant to heat, insects, drought or flooding, they can make huge improvements to yields and profits for farmers, or alternatively make a plant viable to grow somewhere it couldn’t before.
“There are big decreases to yields in equatorial areas — and it’s not that corn kernels are getting smaller,” said co-founder and CEO Brendan Collins. “Farmers move upland because salt water intrusion is disrupting fields, but they run into early spring frosts that kill their seedlings. Or they need rust resistant wheat to survive fungal outbreaks in humid, wet summers. We need to create new varieties if we want to adapt to this new environmental reality.”
To make those improvements in a systematic way, researchers emphasize existing traits in the plant; this isn’t about splicing in a new gene but bringing out qualities that are already there. This used to be done by the simple method of growing several plants, comparing them, and planting the seeds of the one that best exemplifies the trait — like Mendel in Genetics 101.
Nowadays, however, we have sequenced the genome of these plants and can be a little more direct. By finding out which genes are active in the plants with a desired trait, better expression of those genes can be targeted for future generations. The problem is that doing this still takes a long time — as in a decade.
The difficult part of the modern process stems (so to speak) from the issue that traits, like survival in the face of a drought, aren’t just single genes. They may be any number of genes interacting in a complex way. Just as there’s no single gene for becoming an Olympic gymnast, there isn’t one for becoming drought-resistant rice. So when the companies do what are called genome-wide association studies, they end up with hundreds of candidates for genes that contribute to the trait, and then must laboriously test various combinations of these in living plants, which even at industrial rates and scales takes years to do.

“The ability to just find genes and then do something with them is actually pretty limited as these traits become more complicated,” said Mariano Alvarez, co-founder and CSO of Avalo. “Trying to increase the efficiency of an enzyme is easy, you just go in with CRISPR and edit it — but increasing yield in corn, there are thousands, maybe millions of genes contributing to that. If you’re a big strategic [e.g., Monsanto] trying to make drought-tolerant rice, you’re looking at 15 years, 200 million dollars … it’s a long play.”
This is where Avalo steps in. The company has built a model for simulating the effects of changes to a plant’s genome, which they claim can reduce that 15-year lead time to two or three and the cost by a similar ratio.
“The idea was to create a much more realistic model for the genome that’s more evolutionarily aware,” said Collins. That is, a system that models the genome and genes on it that includes more context from biology and evolution. With a better model, you get far fewer false positives on genes associated with a trait, because it rules out far more as noise, unrelated genes, minor contributors and so on.
He gave the example of a cold-tolerant rice strain that one company was working on. A genomewide association study found 566 “genes of interest,” and to investigate each costs somewhere in the neighborhood of $40,000 due to the time, staff and materials required. That means investigating this one trait might run up a $20 million tab over several years, which naturally limits both the parties who can even attempt such an operation, and the crops that they will invest the time and money in. If you expect a return on investment, you can’t spend that kind of cash improving a niche crop for an outlier market.
“We’re here to democratize that process,” said Collins. In that same body of data relating to cold-tolerant rice, “We found 32 genes of interest, and based on our simulations and retrospective studies, we know that all of those are truly causal. And we were able to grow 10 knockouts to validate them, three in a three-month period.”
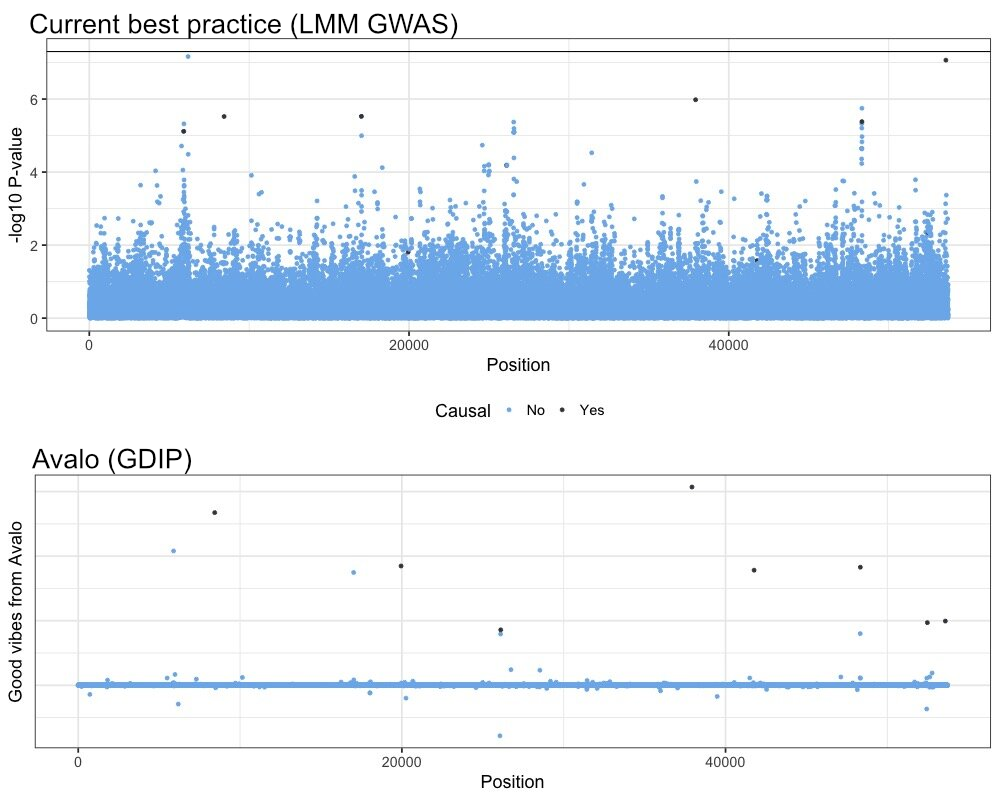
To unpack the jargon a little there, from the start Avalo’s system ruled out more than 90% of the genes that would have had to be individually investigated. They had high confidence that these 32 genes were not just related, but causal — having a real effect on the trait. And this was borne out with brief “knockout” studies, where a particular gene is blocked and the effect of that studied. Avalo calls its method “gene discovery via informationless perturbations,” or GDIP.
Part of it is the inherent facility of machine learning algorithms when it comes to pulling signal out of noise, but Collins noted that they needed to come at the problem with a fresh approach, letting the model learn the structures and relationships on its own. And it was also important to them that the model be explainable — that is, that its results don’t just appear out of a black box but have some kind of justification.
This latter issue is a tough one, but they achieved it by systematically swapping out genes of interest in repeated simulations with what amount to dummy versions, which don’t disrupt the trait but do help the model learn what each gene is contributing.

“Using our tech, we can come up with a minimal predictive breeding set for traits of interest. You can design the perfect genotype in silico [i.e., in simulation] and then do intensive breeding and watch for that genotype,” said Collins. And the cost is low enough that it can be done by smaller outfits or with less popular crops, or for traits that are outside possibilities — since climate change is so unpredictable, who can say whether heat- or cold-tolerant wheat would be better 20 years from now?
“By reducing the capital cost of undertaking this exercise, we sort of unlock this space where it’s economically viable to work on a climate-tolerant trait,” said Alvarez.
Avalo is partnering with several universities to accelerate the creation of other resilient and sustainable plants that might never have seen the light of day otherwise. These research groups have tons of data but not a lot of resources, making them excellent candidates to demonstrate the company’s capabilities.
The university partnerships will also establish that the system works for “fairly undomesticated” plants that need some work before they can be used at scale. For instance it might be better to supersize a wild grain that’s naturally resistant to drought instead of trying to add drought resistance to a naturally large grain species, but no one was willing to spend $20 million to find out.
On the commercial side, they plan to offer the data handling service first, one of many startups offering big cost and time savings to slower, more established companies in spaces like agriculture and pharmaceuticals. With luck Avalo will be able to help bring a few of these plants into agriculture and become a seed provider as well.
The company just emerged from the IndieBio accelerator a few weeks ago and has already secured $3 million in seed funding to continue their work at greater scale. The round was co-led by Better Ventures and Giant Ventures, with At One Ventures, Climate Capital, David Rowan and of course IndieBio parent SOSV participating.
“Brendan convinced me that starting a startup would be way more fun and interesting than applying for faculty jobs,” said Alvarez. “And he was totally right.”






























Comment